Figure 3. pqn-47 mutations and alignment with animal orthologues and spurious yeast homologues.
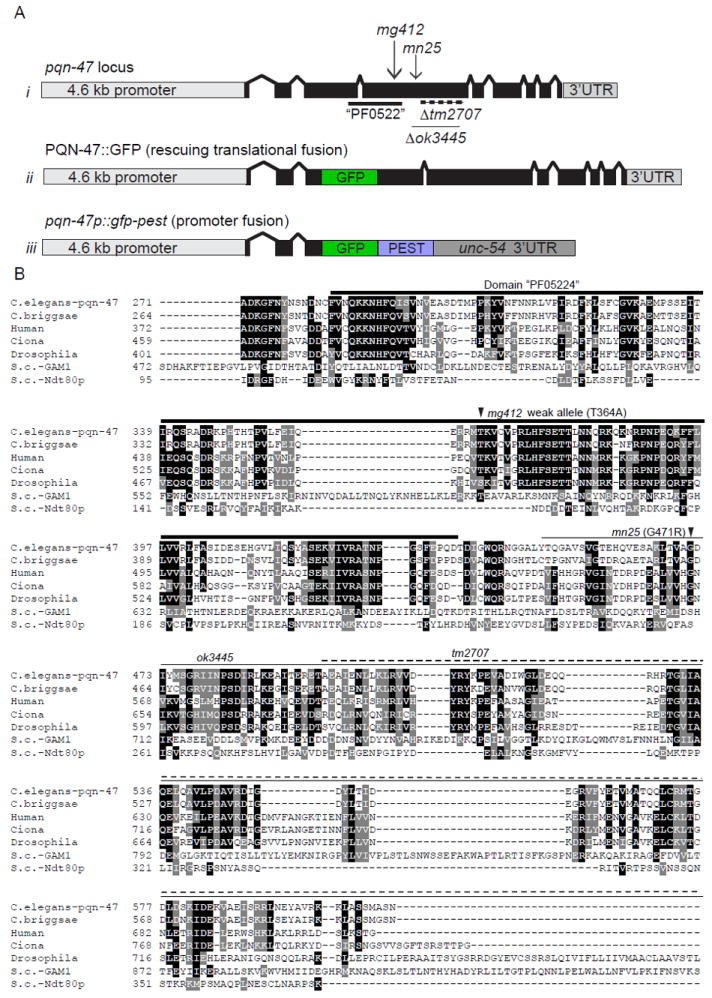
(A) schematic of i) the pqn-47 locus with location of alleles (described in Table. S1) ii) PQN-47∷GFP, a rescuing translational fusion with GFP inserted into a nonconserved region of the third exon iii) a pested promoter pqn-47 fusion. (B) The PQN-47 protein is highly conserved in animals, especially around the central domain PF05224 (thick line) in which all of our mutations are located, but not significantly in fungi. Identical residues shaded black and similar with gray. Arrow heads indicate locations of point mutations mg412 and mn25, and deletions are indicated by a thin line (ok3445) or dashed line (tm2707). GFP was inserted in frame in the coding sequence in an area of low conservation to generate the translational protein fusion used in this study, as C terminal fusions were not able to rescue the mutant phenotypes (data not shown). Full protein sequence shown in figure S2. Protein alignment by CLUSTAL W (2), then BOXSHADE 3.21
