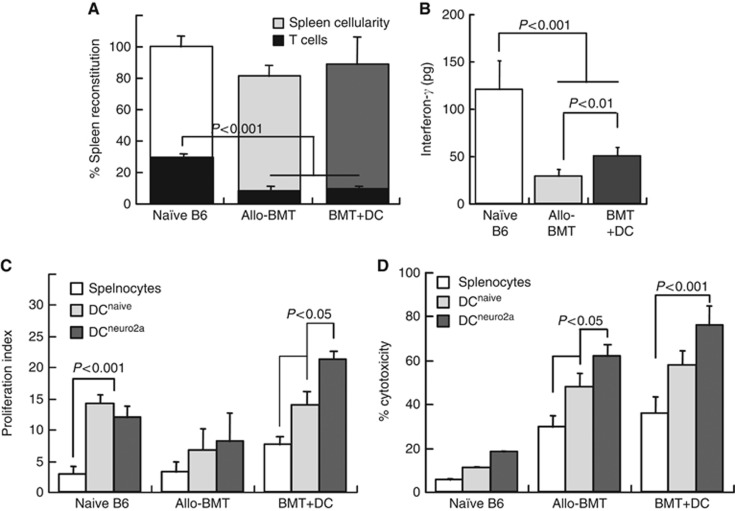
Figure 2.
The impact of immunisation with donor DC on quantitative and qualitative immune reconstitution. Comparative analysis of tumour-bearing mice undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (allo-BMT) and with immunisation using donor DC on day +7 (BMT+DC), as compared with naïve C57Bl/6 control mice without any experimental manipulation. Spleens were evaluated at 4 weeks post transplant for: (A) Reconstitution of spleen cellularity and fractions of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells at 4 weeks after allogeneic BMT (n=7) and following immunisation with tumour-pulsed donor DC (n=7), as compared with naïve B6 donors (n=5). (B) Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) secretion in the corresponding experimental groups (n=4 in each group). (C) Proliferation of splenic lymphocytes in response to mitogenic stimulation with ConA as determined from CFSE dilution and quantified with the ModFit software: naïve B6 mice (n=5), allografted mice (n=8) and with DC immunisation (n=9). (D) Neuro-2a cell lysis by effector lymphocytes from spleens of mice in the three experimental groups, and with restimulation in vitro using naïve (antigen-inexperienced, DCnaive) and tumour-pulsed donor DC (DCNeuro2a). Tumour cell lysis was determined from LDH release by splenic lymphocytes at a target:effector ratio of 1 : 50 representing five mice in each group.