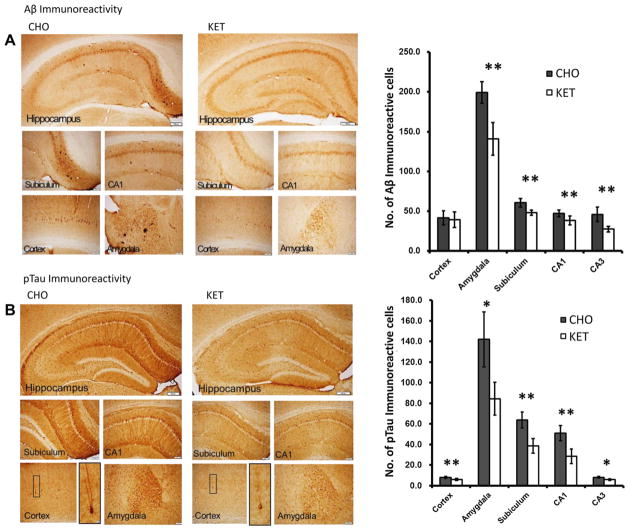
Fig. 6.
Ketone ester feeding reduces intracellular accumulations of amyloid β (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau (pTau) in the subiculum, CA1 and CA3 area of hippocampus, amygdala, and cerebral cortex of 3xTgAD mice. (A) Aβ immunoreactivity in brain sections from mice in the carbohydrate-enriched (CHO; left) and ketone ester (KET; right) diet groups. The upper panels are low magnification images of the regions of the hippocampus and the lower panels are high magnification images of the regions of the subiculum, CA1, cerebral cortex, and amygdala. The graph on the right shows the results of counts of Aβ immunoreactive cells in the indicated brain regions. (B) pTau immunoreactivity in brain sections from mice in the CHO (left) and KET (right) diet groups. The upper panels are low magnification images of the regions of the hippocampus and the lower panels are high magnification images of the regions of the subiculum, CA1, cerebral cortex, and amygdala respectively. The graph on the right shows the results of counts of pTau immunoreactive cells in the indicated brain regions. Scale bars: lower magnification images, 200 μm; high magnification images, 100 μm. Values are the mean ± SEM (n = 6–9 mice per group). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001 by the Student t test.