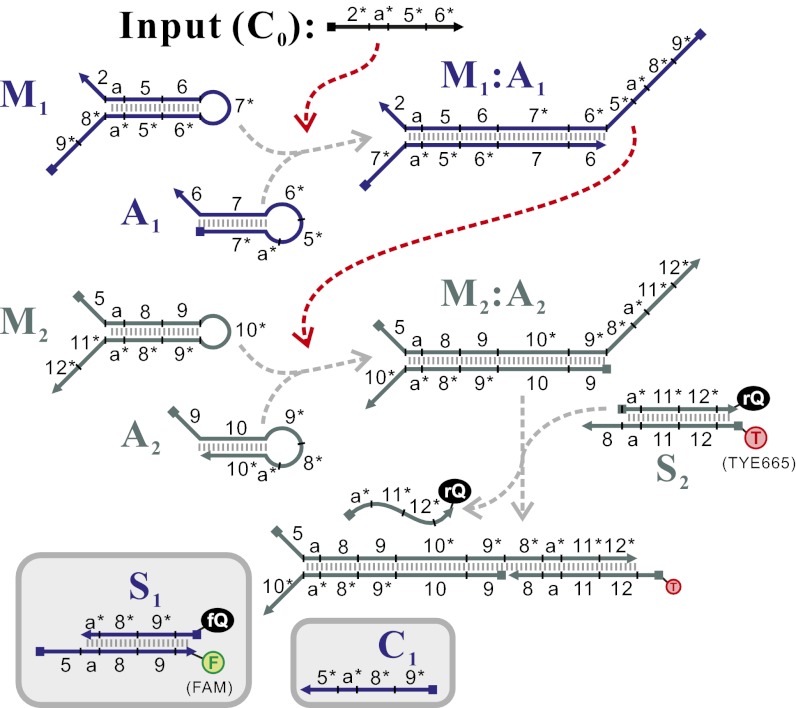
Fig. 1.
Cascading of the CHA reaction. In the first-layer reaction C0 catalyzes the formation of M1:A1 from substrate hairpins M1 and A1. (See Fig. S1 for the detailed pathway of this reaction.) The formation of M1:A1 exposes the 5* toehold domain of M1, enabling M1:A1 to catalyze the formation of M2:A2 in the second-layer reaction. The formation of M2:A2 can be sensed by using a fluorescent reporter S2. Hairpins of the same layer are shown in the same color. (Insets in gray) Additional reagents that are useful in testing individual CHA reactions (such as C1 and S2). Gray dashed arrows connect reactants and products, whereas red dashed arrows connect catalysts and catalyzed reactions. This two-layer cascade can be abbreviated using the presentation shown in the second row of Fig. 2A.