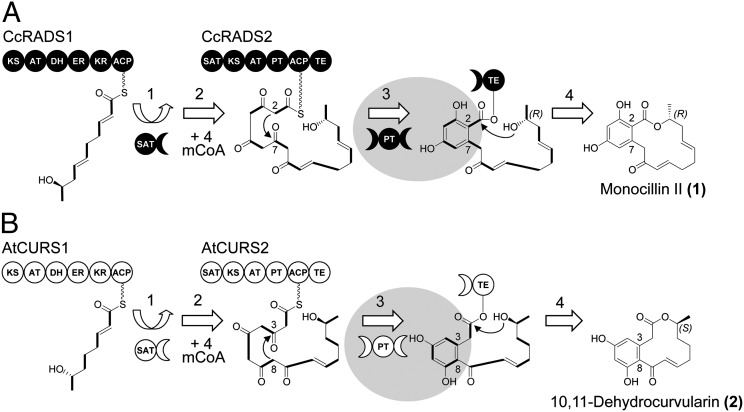
Fig. 1.
Biosynthesis of monocillin II (1) and 10,11-dehydrocurvularin (2). (A) During the biosynthesis of the radicicol intermediate monocillin II (1) in C. chiversii (14), the hrPKS CcRADS1 produces a reduced pentaketide starter unit (13) that is transferred to the nrPKS CcRADS2 by the starter unit:ACP transacylase (SAT) domain (9) (step 1). After another four successive condensation events with malonyl-CoA (mCoA; step 2) catalyzed by the ketoacyl synthase of the nrPKS CcRADS2, the linear ACP-bound polyketide chain undergoes a C2-C7 aldol condensation catalyzed by the PT domain (10) (step 3). This condensation follows an F-type folding mode (28, 29); 1 is released by macrolactone formation catalyzed by the TE domain (2) (step 4). (B) Assembly of 2 in A. terreus AH-02–30-F7 also involves sequentially acting collaborating iPKSs. However, the hrPKS AtCURS1 produces a reduced tetraketide starter, whereas the AtCURS2 PT domain catalyzes aldol condensation in the C8-C3 register using an S-type folding mode (28). C-C bonds in bold indicate intact acetate equivalents (malonate-derived C2 units) incorporated into the polyketide chain by the iPKSs.