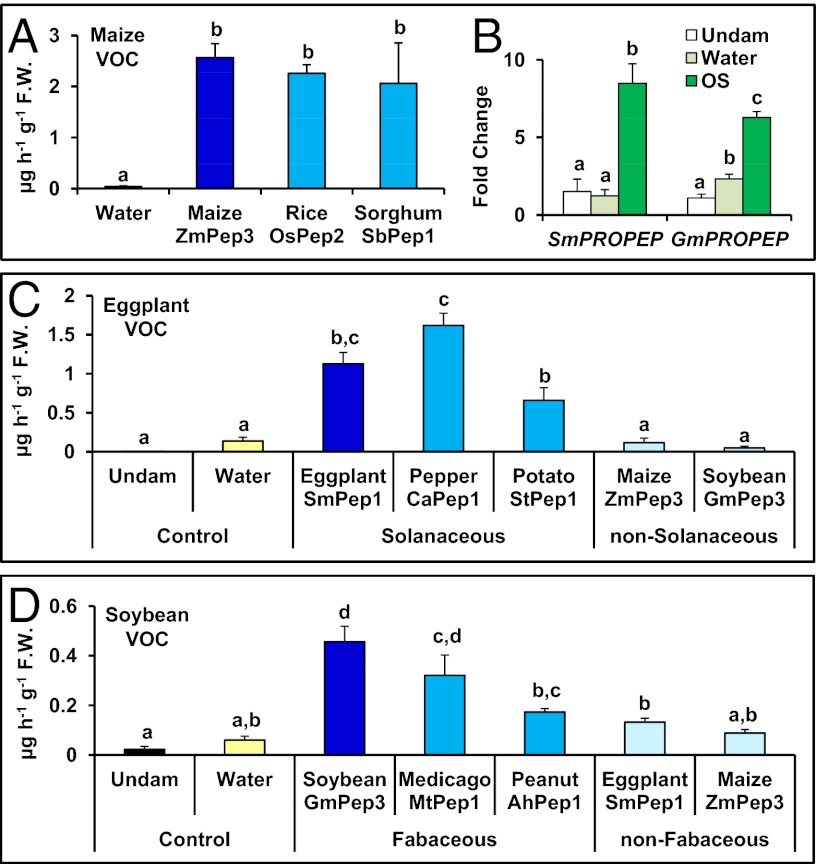
Fig. 5.
Plant elicitor peptides exhibit conserved volatile-inducing activity in related plant species, but limited functionality between distant plant families. (A) Total emitted volatiles from maize leaves 16 h posttreatment with water or with Peps from maize, rice, and sorghum. (B) Relative expression as determined by qRT-PCR of the genes encoding the peptide precursor proteins from eggplant (SmPROPEP1) or soybean (GmPROPEP3) in eggplant or soybean leaves that were untreated (white) or 30 min posttreatment with either water (light green) or S. exigua OS (dark green). (C) Volatiles emitted from undamaged eggplant leaves or from scratch-wounded leaves 5 h posttreatment with water or Peps from Solanaceous or non-Solanaceous species. (D) Volatiles emitted from undamaged soybean leaves or from scratch-wounded leaves 5 h posttreatment with water or Peps from Fabaceous or non-Fabaceous species. For all experiments, peptides were used at 2 nmol⋅g−1 FW. Within each plot, different letters (a–d) represent significant differences between mean values (n = 4, ± SEM; all ANOVAs, P < 0.001; Tukey test corrections for multiple comparisons, P < 0.05).