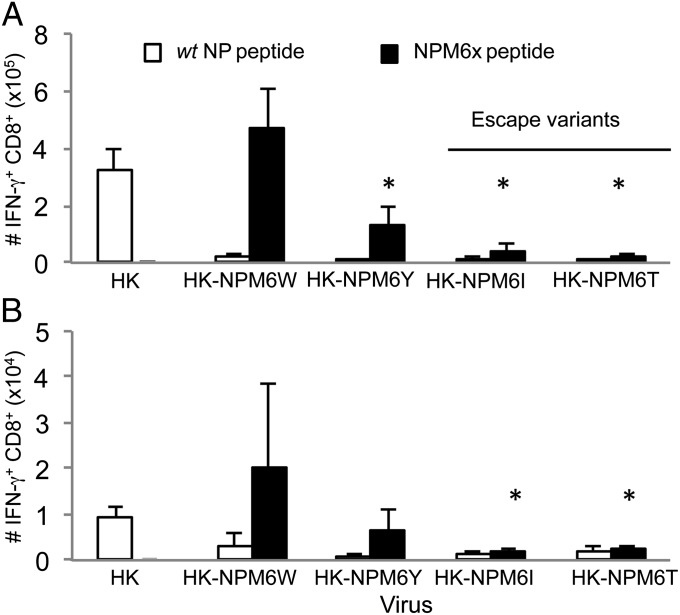
Fig. 1.
The NPM6W and NPM6Y mutants (but not the NPM6I or NPM6T escape variants) generate unique CD8+ T-cell responses. Following intranasal infection with either the WT HK or mutant HK-NPM6X virus, (A) splenocytes or (B) BAL cells (from the site of infection) were stimulated with the WT NP or NPM6X peptides corresponding to the infecting virus. The numbers of epitope specific CD8+ T cells were calculated from the percentage of cells staining and the total cell counts. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 5). Representative FACS plots and the actual numbers of epitope-specific CD8+ T-cell populations are shown in Fig. S2. Experiments were repeated at least twice. *P ≤ 0.01 relative to WT DbNP366+CD8+ response.