Figure 3. Synaptic potentiation initiated by cue-induced cocaine seeking.
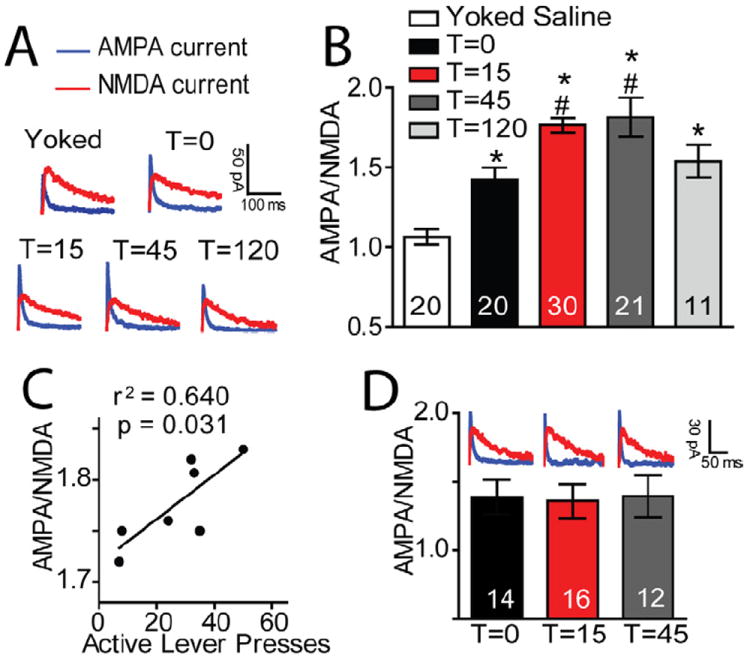
(A) Sample AMPA and NMDA current traces from each group. (B) AMPA to NMDA ratios (A/N) were significantly elevated in animals withdrawn with extinction training from cocaine self-administration (1.423 ± 0.075) compared to yoked saline animals (1.064 ± 0.050). In addition, the initiation of cue-induced reinstatement further elevated A/N at T=15 (1.780 ± 0.060). Ratios remained elevated at T=45 (1.815 ± 0.122), and returned to pre-reinstatement levels by T=120 (1.538 ± 0.103) (F(4,101)= 14.45, P< 0.001). (C) The increase in A/N at 15 min was significantly correlated with the number of active lever presses. (D) Cue-induced reinstatement of sucrose seeking did not alter A/N. Two to five neurons were recorded from each animal. Data are shown as mean ± SEM.
*p< 0.05 compared to yoked saline animals at T=0 (white bar); #p< 0.01 compared to T=0 (black bar).
