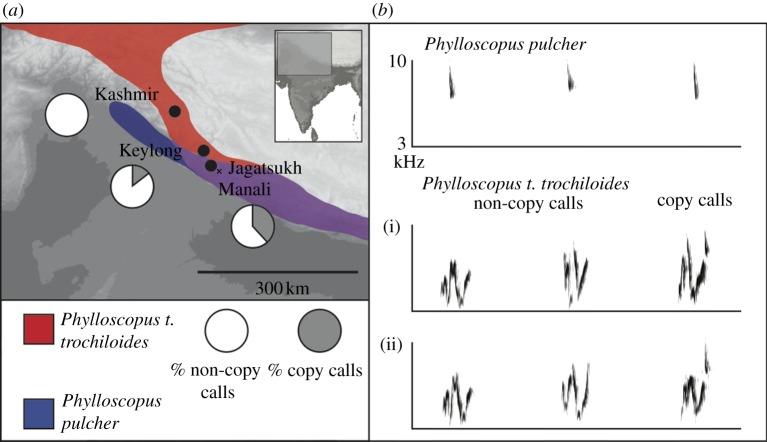
Figure 2.
(a) Field sites in the Indian Himalayas included in the study. Shading indicates 1000 m elevation bands. Manali is divided into two areas: a lower elevation area (3100–3450 m) with 15 commonly mobbing species and a higher elevation area (more than 3450 m), with only two commonly mobbing species, Phylloscopus t. trochiloides and Phylloscopus pulcher. Breeding ranges of these two species are given in colour (modified from [20]), showing the percentage of calls used by P. t. trochiloides that copy the call of P. pulcher (high-elevation Manali: 41%; Keylong: 13%; Pakistan: 0%, [21]). (b) Representative mobbing calls produced by P. pulcher and P. t. trochiloides. Phylloscopus trochiloides trochiloides individuals (i) and (ii) produce both non-copying calls and calls that incorporate the call of P. pulcher.