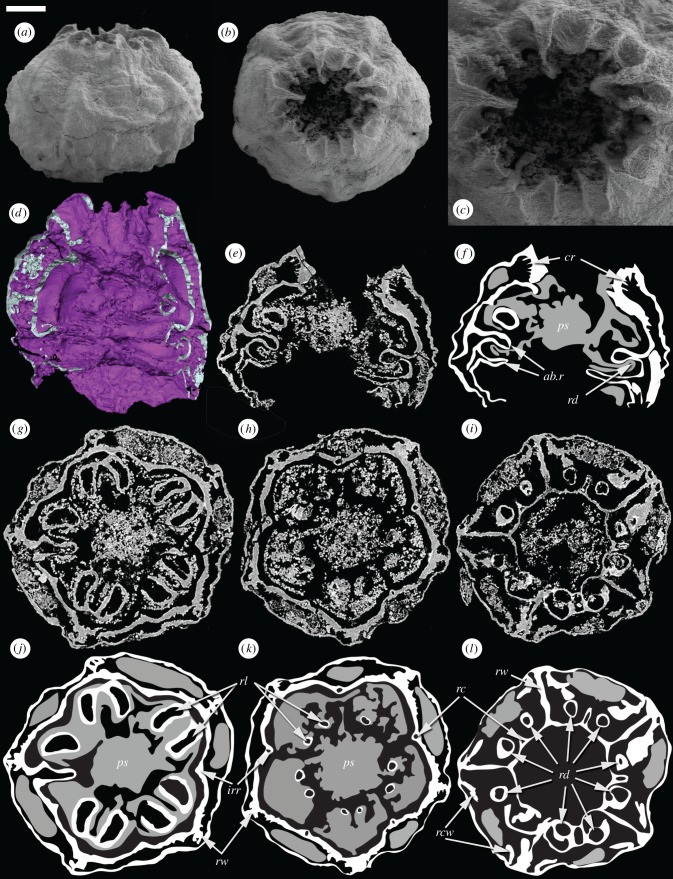
Figure 3.
Embryonic Olivooides specimen with internal preservation (GMPKU3089) imaged using SEM (a–c) and SRXTM (d–l). (a) Whole specimen in lateral view. (b) Whole specimen in apertural view. (c) Detail of the aperture. (d) Surface rendering showing the internal anatomy. (e,f) Longitudinal section and interpretative drawing. (g,j) Transverse section and interpretative drawing showing paired projections from the inner wall and radial structures that connect the inner and outer walls. (h,k) Transverse section and interpretative drawing in particular showing interadial canals. (i,l) Transverse section and interpretative drawing showing the inner wall extending into the lumen to form the upper abradial ridge; depressions in the lower surface of the ridge appear as paired circular structures in section. Within the interpretative drawings, white represent a dense highly X-ray attenuating mineral phase, while grey reflects a more diffuse lowly attenuating mineral phase; both are interpreted to reflect original biological structure. ab.r, abradial ridges; cr, circumferential ridges; irr, interradial ridge; ps, polygonal axial structure; rc, radial canal; rcw, recurved wall; rd, radial depression; rl, radial lobe; rw, radial wall. Scale bars: (a,b) 153 µm, (c) 73 µm, (d) 78 µm, (e,f) 124 µm, (g,j) 119 µm, (h,k) 136 µm, (i,l) 143 µm. (Online version in colour.)