Fig. 1.
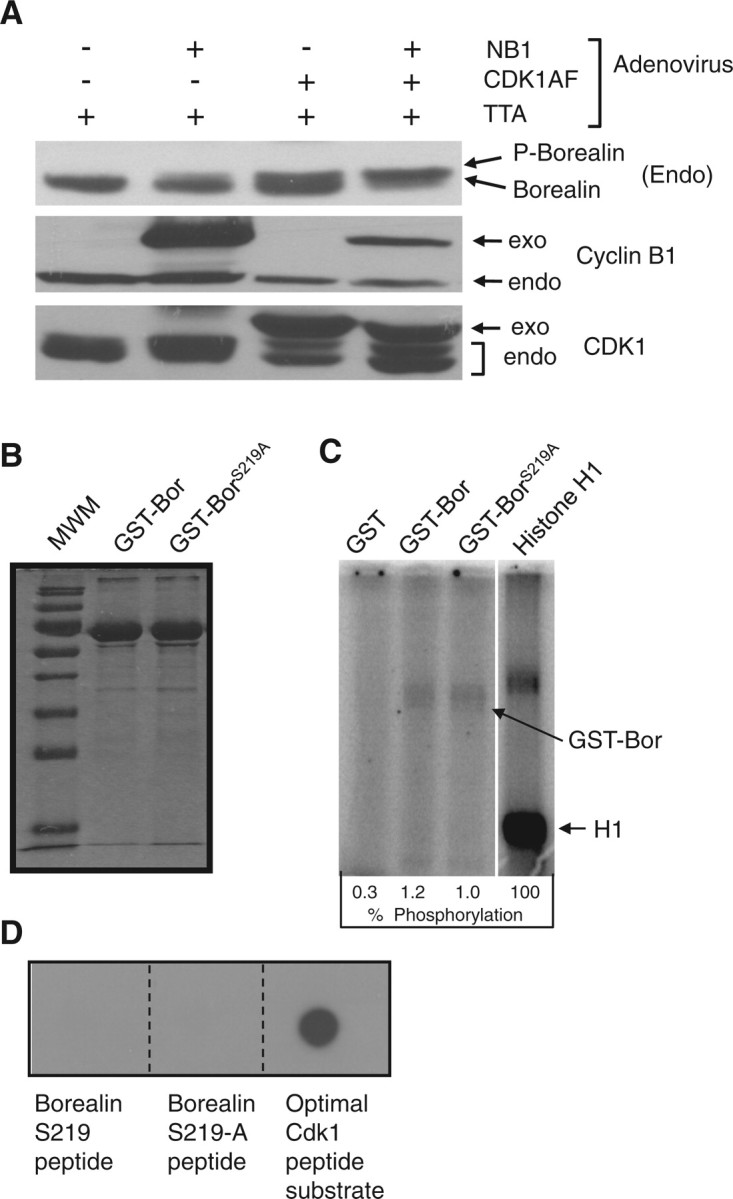
Effect of Cdk1 on Borealin phosphorylation. (A) Cdk1/Cyclin B1 induces Borealin mobility shift. HeLaM cells were blocked in S phase with hydroxyurea and then infected with recombinant adenoviruses as indicated at an MOI of 50. TTA virus encodes the tetracycline activator needed for expression from the recombinant adenoviruses. NB1, nuclear targeted Cyclin B1; Cdk1AF, Cdk1 T14A,Y15F. Lysates were analysed by western blotting with antibodies to endogenous Borealin, Cyclin B1, Cdk1 and β-actin to control for loading. Exo, exogenous; Endo, endogenous. (B) Purification of Borealin–GST. Wild-type Borealin (GST–Bor) and Borealin S219A (GST–BorS219A) were purified from E. coli as GST fusions. The proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. (C) Phosphorylation of GST–Borealin by Cdk1. GST–Bor, GST–BorS219A, histone H1 and GST were phosphorylated in vitro with purified Cdk1/Cyclin-B1 in the presence γ-(32P)ATP. The proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE followed by autoradiography. Reactions included 1.0 µg of histone H1 which upon Coomassie blue staining was always lower in intensity compared to GST–Borealin (our unpublished data). Extent of phosphorylation is shown as a percent of H1 phosphorylation. (D) Cdk1 does not phosphorylate Borealin peptides. N-terminal biotinylated peptides containing Borealin S219, Borealin S219A and an optimal Cdk1 substrate were phosphorylated in vitro by purified Cdk1/Cyclin-B1 in the presence γ-(32P)ATP. The reactions were spotted on PVDF membrane saturated with avidin. The PVDF membrane was washed and visualized by autoradiography.
