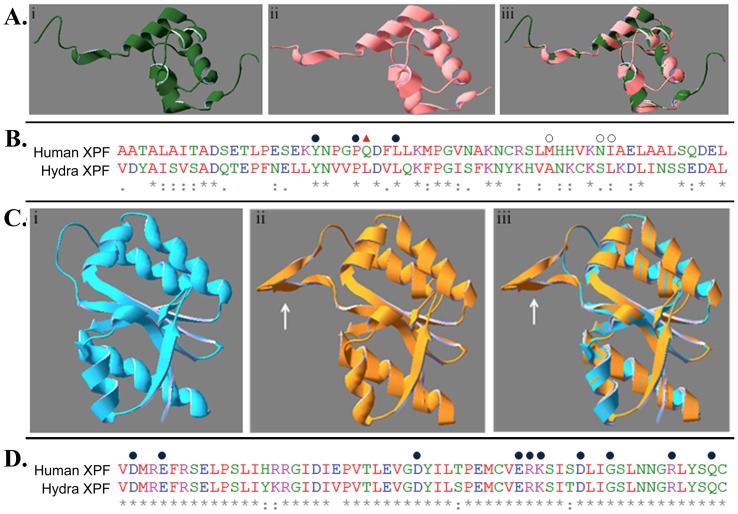
Figure 2. Comparison at structure and sequence levels of hydra XPF regions with corresponding regions from other XPFs. A.
Homology modelling for ERCC1-binding domain. i. Structure of B-chain of human XPF-ERCC1 complex (PDB: 1Z00) ii. Predicted structure of ERCC1-binding region of hydra XPF iii. Overlap of 2Ai, 2Aii. B. Sequence alignment of ERCC-1 interaction domains from human and hydra XPF. 3 out of 7 residues involved in interaction are conserved (filled circle) while 3 more are replaced by conservative substitutions (open circle). The residue at one position (triangle) is not conserved between the two species. C. Homology modelling for the nuclease motif containing ERCC4 domain. i. Structure of P. furiosus endonuclease domain (PDB:1J23) ii. Predicted structure of ERCC4 region of hydra XPF iii. Overlap of 2Ci, 2Cii (arrows show extra pair of β-sheets present in hydra XPF) D. Alignment of sequence around the nuclease motif of human and hydra XPF. Residues important for catalysis (filled circle) are completely conserved between the two species.