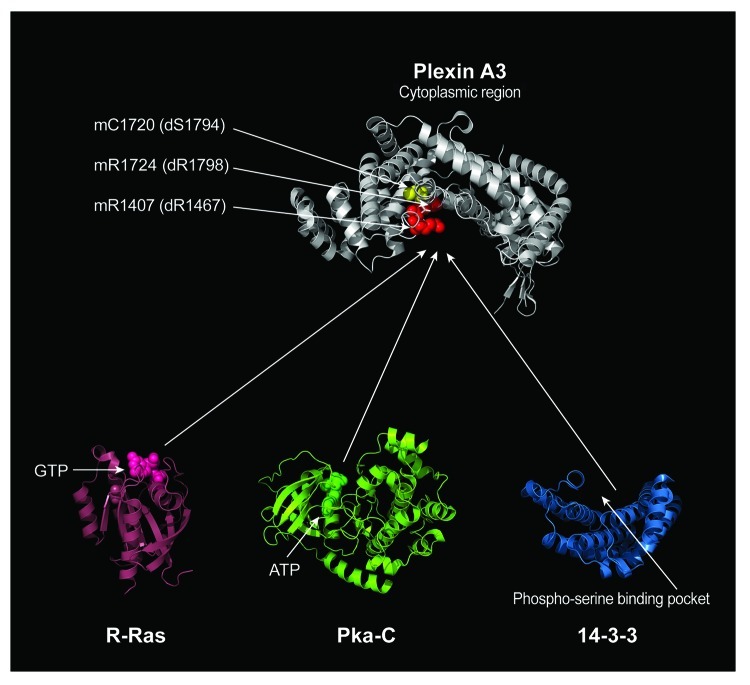
Figure 2. Structural Comparison of Proteins Interacting with the Plexin GAP domain. Our results indicate that Ras family GTPases, 14-3-3ε, and a catalytic subunit of PKA (Pka-C) share a binding site within the GAP domain of Plexin A. The conserved arginine residues that are critical for Plexin RasGAP activity are labeled in red. The residue corresponding to a 14-3-3ε binding site is labeled in yellow, which is veiled by the arginine residues. The amino acid residues for these arginine and serine in both mouse Plexin A3 (m) and Drosophila PlexA (d) are indicated by arrows. The structural model of the Plexin A3 cytoplasmic region (some portions of the cytoplasmic region were not resolved in the crystal structure) is oriented with the concave surface of RasGAP domain facing downward. Active sites for proteins that interact with the Plexin RasGAP domain are indicated such as GTP for R-Ras and ATP for Pka-C. The phospho-serine-binding pocket of 14-3-3 is also indicated (14-3-3 is thought to often function as a dimer and bind two different phosphorylated residues. For clarity, a monomer of 14-3-3 is depicted). Protein data bank identification numbers: 3IG3 for mouse Plexin A3, 2FN4 for human R-Ras, 2F7X for cow catalytic subunit of PKA and 2BR9 for human 14-3-3ε.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.