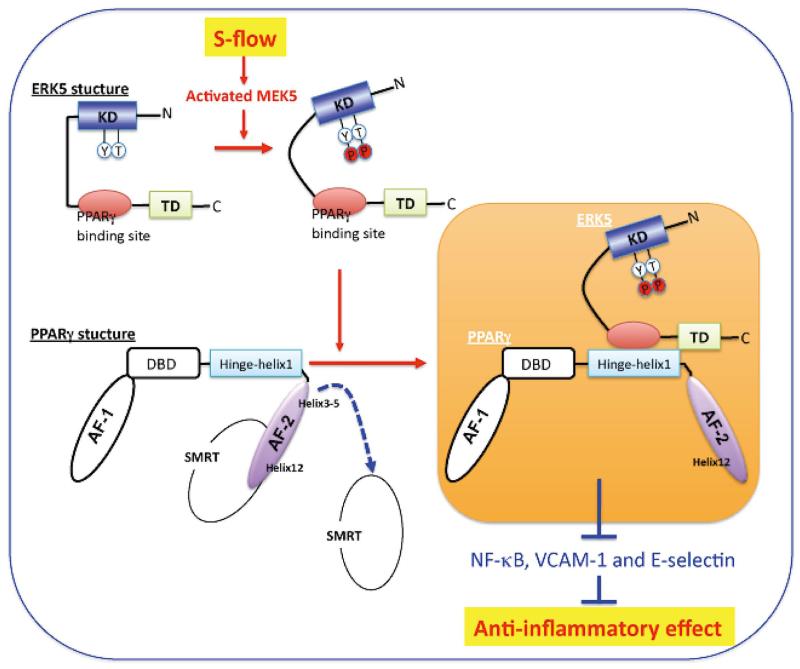
Figure 6.
PPARγ transactivation by ERK5 When the ligand binds to PPARγ, Helix 12 folds back to form a part of the co-activator binding surface and inhibits co-repressor (such as SMRT) binding to PPARγ. The co-repressor interaction surface requires Helix 3-5 region. The inactive N-terminal kinase domain of ERK5 inhibits its own transactivation and PPARγ binding. After ERK5 activation by s-flow stimulation, the inhibitory effect of N-terminal domain of ERK5 decreases, and subsequently the middle region of ERK5 can fully interact with the hinge-helix 1 region of PPARγ. The association of ERK5 with the hinge-helix 1 region of PPARγ releases co-repressor of SMRT and induces full activation of PPARγ. KD, kinase domain; TD, transactivation domain; AF-1/2, activating function (AF)-1/2 transactivation domain, DBD, DNA binding domain. (Modified from Akaike et al,19 Copyright © 2004, American Society for Microbiology, MCB.24.19.8691-8704. 2004, DOI: 10.1128) (See text for details.)