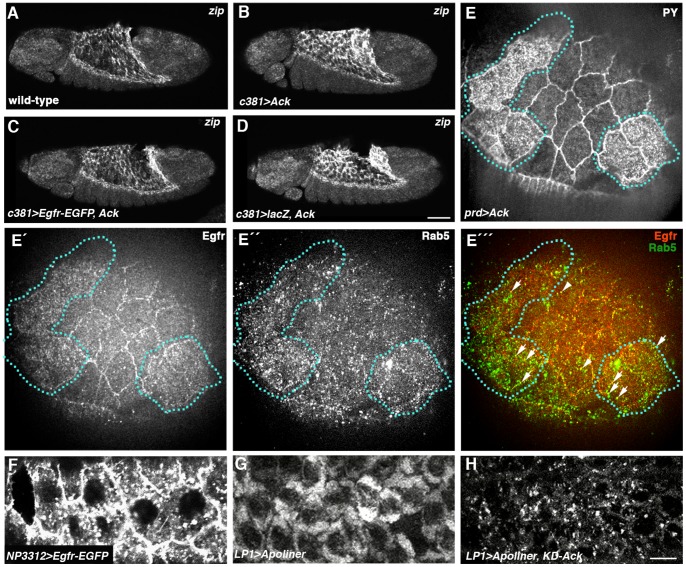
Figure 6. Evidence that Egfr signaling is negatively regulated by endocytosis in the AS.
(A–D) zip FISH on embryos late in germband retraction. (A) Wild-type embryo showing zip expression in AS. (B) Expression of Ack in the AS using the Gal4c381 driver causes an increase in zip levels in this tissue relative to wild-type. (C) Ack fails to elevate zip levels when co-expressed with Egfr–EGFP. (D) zip levels are elevated when Ack is co-expressed with control lacZ gene. (E–É ´´) AS in which Ack had been over-expressed in prd stripes, triple-stained with anti-phosphotyrosine (anti-PY) (E), anti-Egfr (É) and anti-Rab5 (É ´). (E) Cells over-expressing Ack are marked by high levels of anti-PY (outlined with dotted lines). (É) Egfr shows strong cortical localization in wild-type AS cells but a more cytoplasmic distribution in Ack-over-expressing cells. (É ´) There is an increase in Rab5-positive early endosomes in Ack-over-expressing cells. (É ´´) Merge of panels É and É ´. Arrowheads and arrows mark Egfr-positive early endosomes in wild-type cells and Ack-over-expressing cells, respectively. (F) Egfr-EGFP expressed in the AS using the Gal4NP3312 driver shows vesicular accumulation in addition to being at the plasma membrane. (G) AS cells in embryo in which Apoliner has been expressed with LP1-Gal4 driver showing localization of Apoliner-RFP signal to membranes. (H) AS cells in embryo in which Apoliner and kinase-dead Ack have been co-expressed with LP1-Gal4 driver showing punctate localization of Apoliner-RFP signal. Scale bars: 50 µm in A-D; 5 µm in E-H.