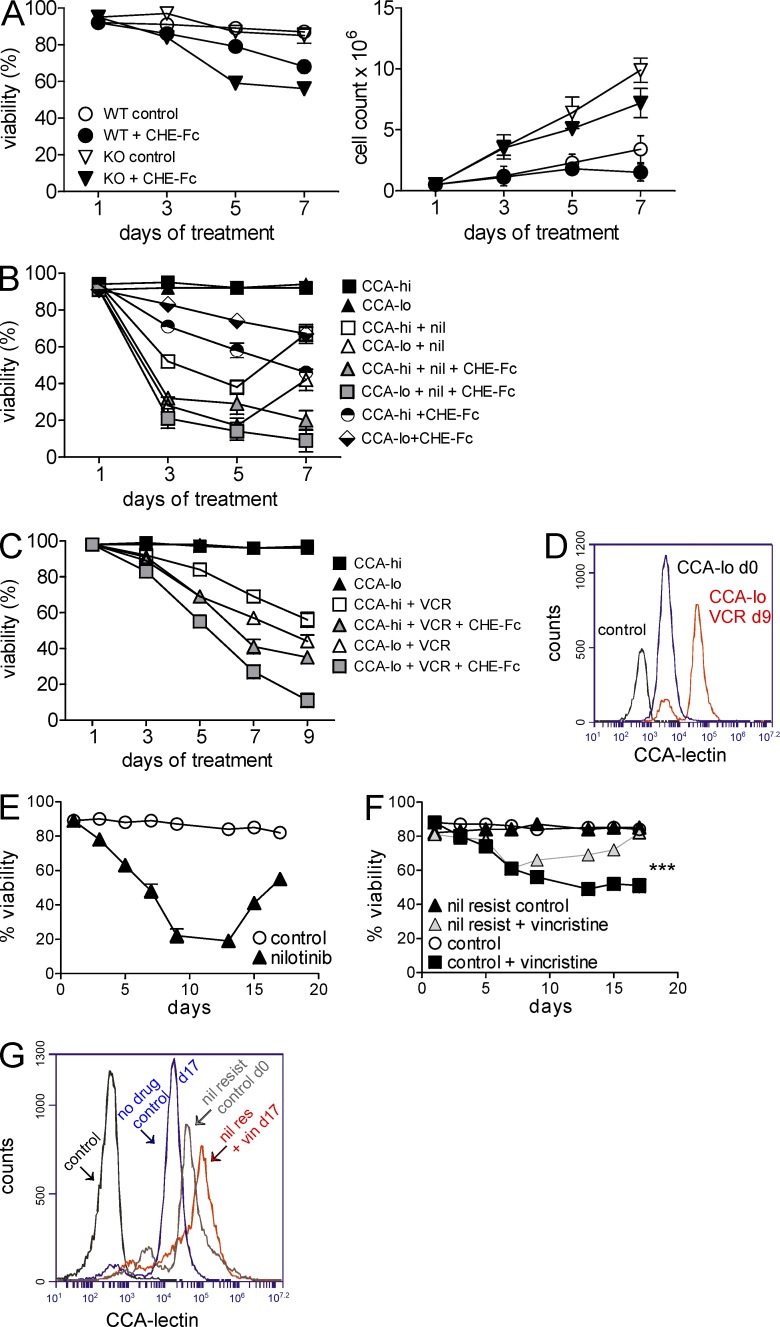
Figure 7.
CHE-Fc acetylesterase treatment sensitizes ALL cells to drugs. (A) Percent viability (left) and cell counts (right) of WT and GD3 KO BCR/ABL-transduced cells treated with 25 µg/ml CHE-Fc. Viability WT versus WT + CHE-Fc: P = 0.0008; KO versus KO-CHE-Fc: P = 0.0009. The experiment was performed twice independently. (B) Percent viability of flow-sorted CCAhi and CCAlo 8093 cells co-cultured with OP9 stroma in the presence or absence of 20 nM nilotinib (nil), 10 µg/ml CHE-Fc, or both. P < 0.001 nil only, CHE-Fc only, and nil + CHE-Fc for CCAhi versus CCAlo on day 9 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. (C) Percent viability of CCAhi and CCAlo US7 cells treated with 5 nM vincristine (VCR) or 5 nM vincristine plus 10 mg/ml CHE-Fc. CCAhi and CCAlo US7 cells were sorted after 22 d of 5-nM vincristine treatment. In both B and C, treatment was continued 24 h after sorting. A single experiment was performed with triplicate samples. Day 9 vincristine and vincristine + CHE-Fc for CCAhi versus CCAlo: P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. (D) CCA lectin detection on CCAlo US7 cells treated with vincristine on day 9 from C, compared with day 0 and unstained cells as indicated. (E and F) Viability of BCR/ABL-transduced WT pre-B cells treated with 24 nM nilotinib every alternate day for 17 d (E) and viability of the nilotinib-resistant cells (on day 17 from E) subsequently treated with 2.5 nM vincristine for 17 d (F). ***, P < 0.001 day 17 control + vincristine versus nil resis + vincristine. (G) CCA lectin–binding cell surface structures detected on cells including nilotinib-resistant controls (in E, day 17 treated = day 0 cells in panel F), vincristine-resistant cells from F on day 17, untreated control cells from day 17 from F, and unstained cells as indicated. Error bars show the standard deviation of triplicate samples.