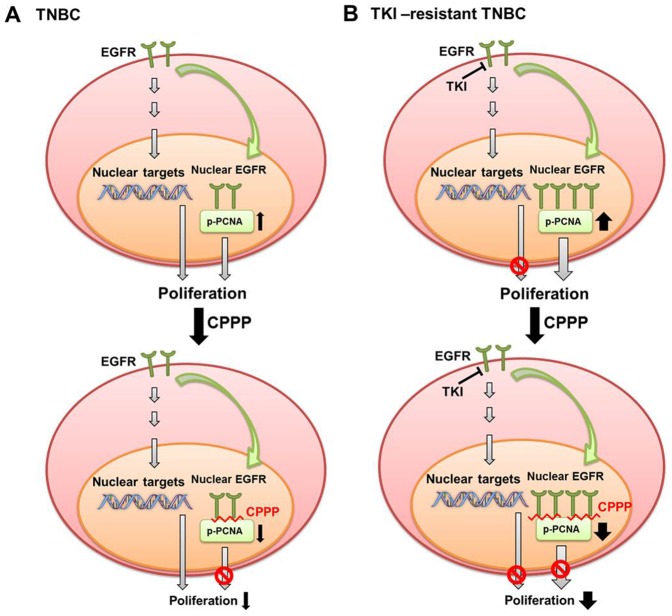
Figure 6. A proposed model of CPPP in TNBC treatment.
The schematic illustrates the potential mechanism of CPPP in treatment of TKI-sensitive and -resistant TNBC. (A) In TNBC, both the classical EGFR membrane signaling and nuclear EGFR-mediated phosphorylation of PCNA at Y211 exist for cell proliferation. CPPP disrupts the nuclear EGFR-mediated PCNA phosphorylation at Y211, leading to suppression of proliferation. (B) In EGFR TKI-resistant TNBC, EGFR TKIs abrogate the classical EGFR membrane signaling, and thus elevate nuclear translocation of EGFR to phosphorylate more PCNA at Y211, triggering more second compartment of proliferation. CPPP attenuates more nuclear EGFR-mediated cell proliferation through repression of Y211 phosphorylation in the presence of EGFR TKIs.