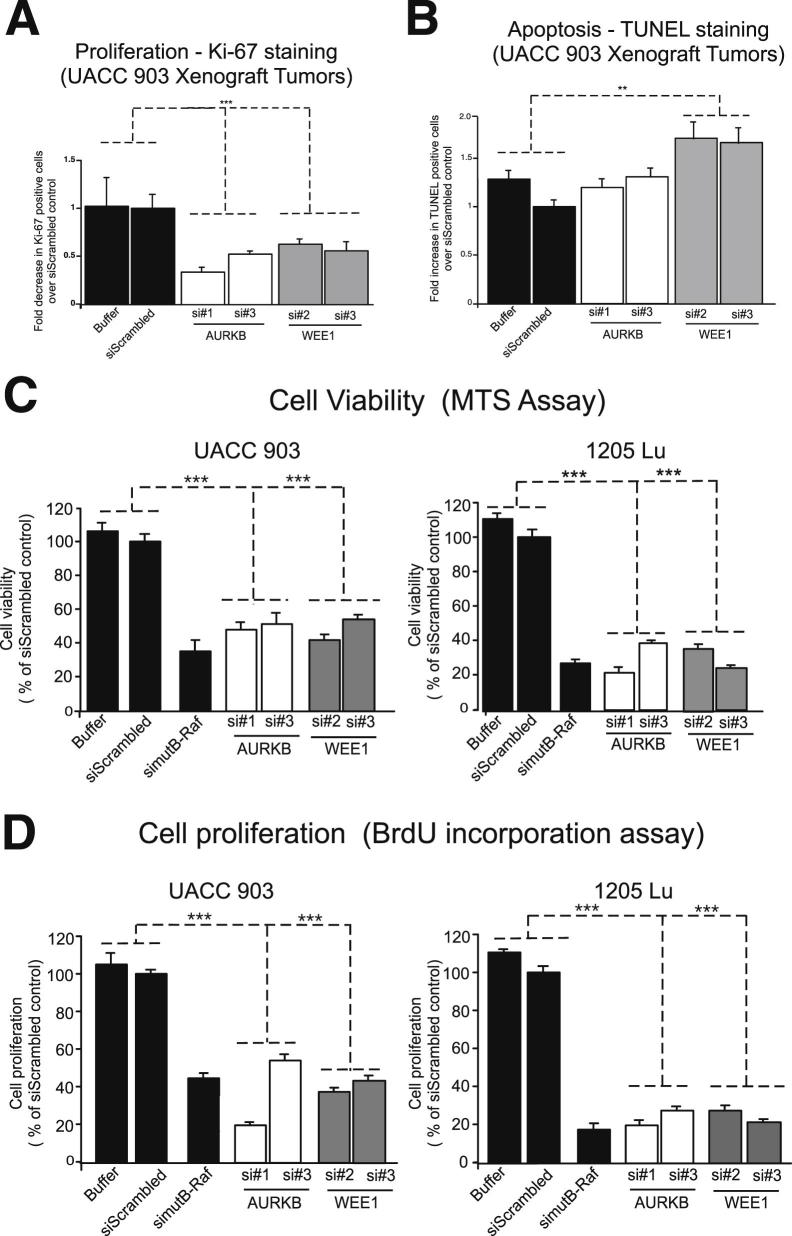
Figure 5.
Targeting AURKB or WEE1 reduced melanoma cell survival by decreasing the proliferative potential of melanoma cells. A and B: Size- and time-matched tumors from animals injected with UACC 903 melanoma cells transfected with buffer or siScrambled controls or siRNA to AURKB or WEE1. Tumor sections were immunostained for Ki-67 (A) or TUNEL (B) for proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. Images were quantified and plotted as fold decrease or increase in Ki-67– or TUNEL-positive cells compared with controls. Data were obtained from three to four tumors, with four to five fields averaged per tumor. C and D: siRNA was introduced in UACC 903 or 1205 Lu melanoma cells and an MTS or BrdU incorporation assay undertaken after 3 days to measure cell viability or proliferation, respectively. V600EB-RAF served as a control of a gene decreasing cell viability. Results represent pooled data from three independent experiments. Data represent means ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.01. ns, not statistically significant. An analysis of variance, followed by a post hoc test, was used.