Figure 1. Unique effector properties of NK cells in the liver.
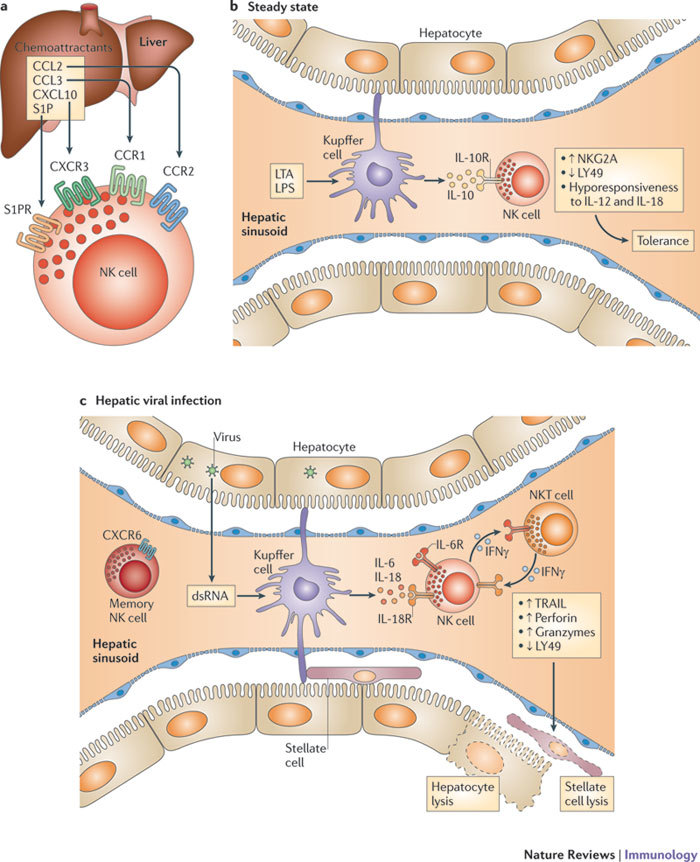
a | CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), CCL3, CXC-chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)125 derived from Kupffer cells and other hepatic cells attract natural killer (NK) cells to the inflamed liver. b | Hepatic NK cells reside in distinctive, thin-walled sinusoids, where Kupffer cells and other lymphocytes are also located. Hepatic NK cells face the challenging task of balancing immunity to multiple hepatotropic viruses and bacteria with tolerance to food and self antigens. In the steady state, commensal-derived lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that arrive in the liver from the gut through the portal vein ligate Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4, respectively, on Kupffer cells, triggering the release of interleukin-10 (IL-10)126. IL-10 in turn renders NK cells hyporesponsive to IL-12 and IL-18 and promotes tolerance in the liver. In addition, expression of the inhibitory receptor natural killer group 2, member A (NKG2A) is increased, whereas expression of the activating receptor LY49 is decreased on NK cells. c | During viral infection, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) ligates TLR3 and triggers Kupffer cells to release IL-6 and IL-18, which in turn activate NK cells and boost their killing activity. This is reflected by the phenotype of hepatic NK cells, which is characterized by the expression of high levels of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), perforin and granzymes, and a lack of LY49. Activated hepatic NK cells can lyse hepatocytes or stellate cells via TRAIL-dependent pathways during hepatitis B virus infection or fibrosis, respectively. Thus, Kupffer cells appear to have a dual role in shaping hepatic NK cell phenotype and function. Hepatic NK cells are also subjected to the influence of interferon-γ (IFNγ) released by natural killer T (NKT) cells. Hepatic NK cells can acquire memory to antigens derived from influenza virus, vesicular stomatitis virus and HIV-1 (not shown). CCR, CC-chemokine receptor; CXCR, CXC-chemokine receptor; S1PR, S1P receptor.
