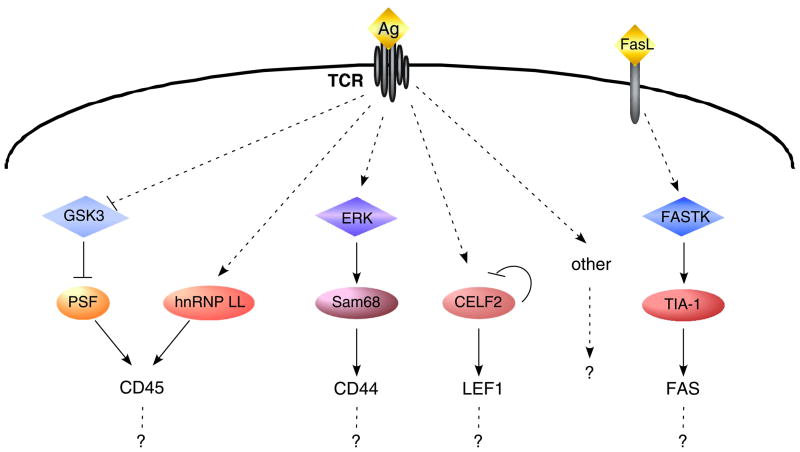
Fig. 5. Networks of signaling pathways that regulate AS in T cells.
Summary of several known kinases (blue/purple diamonds) and RNA binding factors (orange/red ovals) that have been shown to be regulated in response to antigen (Ag) stimulation or Fas Ligand (FasL) signaling in T cells, and the genes (text) that they regulate. Solid arrows and lines indicate direct activities, dotted arrows/lines indicate known relationships that are likely indirect. ‘other’ indicates the fact that there are likely many other signaling pathways that are also involved in mediating antigen-induced changes in AS that are yet to be discovered. Question marks are meant to emphasize that although each signaling pathway so far has only been linked to regulation of 1–2 genes, each branch likely regulates a program of co-regulated genes. Cross-coordination between branches is also anticipated, as observed for CD45. See text for detailed description of each pathway.