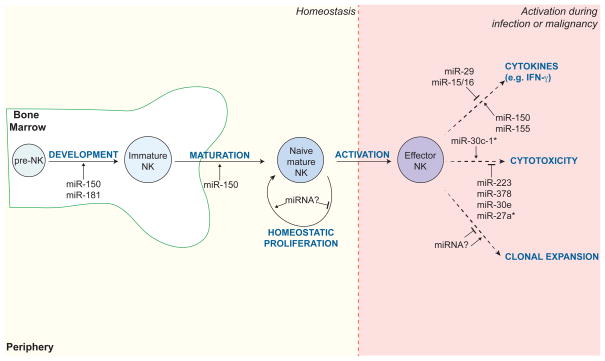
Fig. 6. miRNAs regulate the development, maturation, and effector function of NK cells.
A summary of individual miRNAs known to regulate NK cell development and function at steady state and in the context of activation (e.g. during infection or malignancy). Examples include miR-150 and miR-181, which are required for NK cell development and maturation in the bone marrow; miR-150, miR-155, miR-29, and miR-15/16, which modulate cytokine production by activated NK cells; and miR-30c-1*, miR-223, miR-378, miR-30e, miR-27a*, which control expression of cytotoxic molecules, such as granzyme B and perforin.