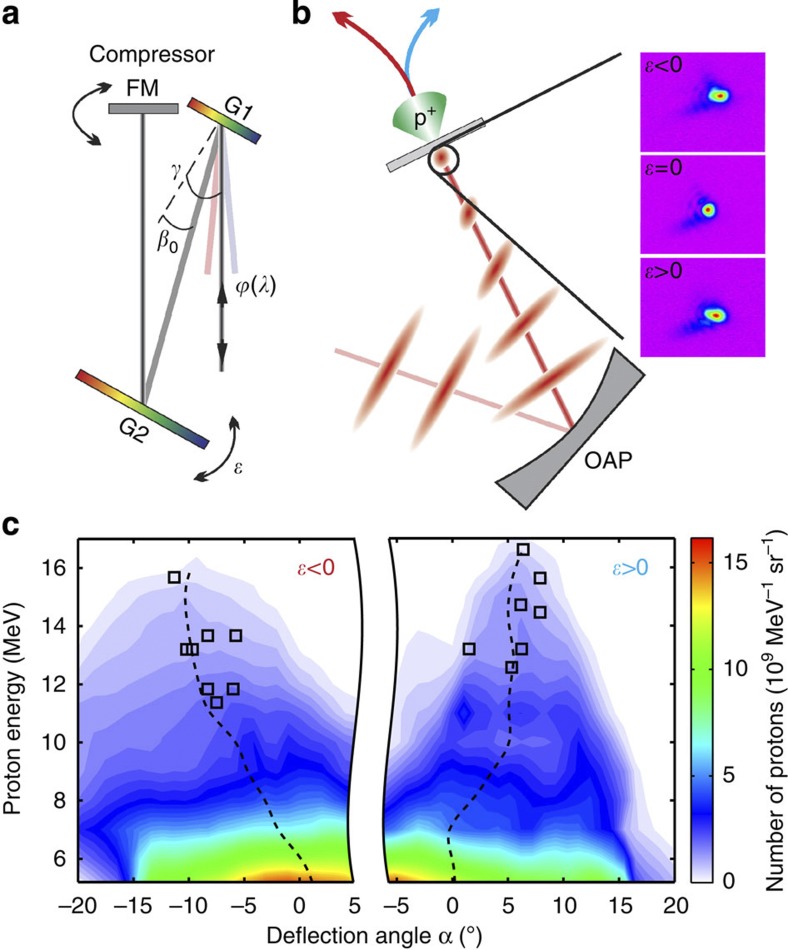
Figure 3. Set-up and results of the test experiment.
(a) Grating compressor consisting of the gratings G1 and G2 and the folding mirror FM. The incidence angle γ and the diffraction angle β0 are necessary to calculate the angular chirp d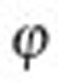 /dλ (equivalent to pulse front tilt) generated by a slight tilt of G2 by the angle
/dλ (equivalent to pulse front tilt) generated by a slight tilt of G2 by the angle 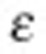 (see Methods). (b) The tilted intensity envelope is focussed by the off-axis parabola (OAP) under normal incidence onto a 2-μm thick Ti-foil target. The spatial chirp in the focal plane caused by the angular chirp results in horizontally enlarged focal spots, as displayed in the three images for the according settings of
(see Methods). (b) The tilted intensity envelope is focussed by the off-axis parabola (OAP) under normal incidence onto a 2-μm thick Ti-foil target. The spatial chirp in the focal plane caused by the angular chirp results in horizontally enlarged focal spots, as displayed in the three images for the according settings of 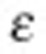 . (c) On the basis of the change of sign in the designed pulse front tilt, the most energetic protons are deflected away from the target normal, as it is shown by two samples of reconstructed angular proton spectra for
. (c) On the basis of the change of sign in the designed pulse front tilt, the most energetic protons are deflected away from the target normal, as it is shown by two samples of reconstructed angular proton spectra for 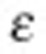 >0 and
>0 and 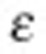 <0. Black squares represent the scattering of the deflection angle of the most energetic protons for the full series of shots. The dashed line follows the centroid of the angular distribution.
<0. Black squares represent the scattering of the deflection angle of the most energetic protons for the full series of shots. The dashed line follows the centroid of the angular distribution.