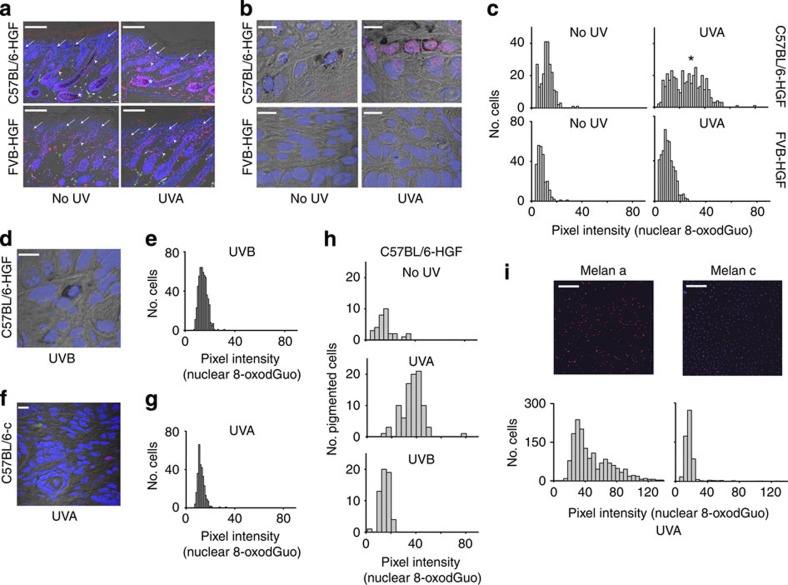
Figure 5. Ultraviolet A induced oxidative DNA damage in neonatal skin and cultured melanocytes.
(a) Extra-follicular melanocytes (arrows) show increased nuclear 8-oxodGuo (pink) after 150 kJ m−2 of ultraviolet A in C57BL/6-HGF but not in FVB-HGF skin. Nuclear 8-oxodGuo is visible in all panels in the hair follicle outer root sheath (white arrowheads) and in the hair bulb of C57BL/6-HGF-pigmented skin where it is increased by ultraviolet A (asterisks) but is sparse in the hair bulb of albino FVB-HGF skin. Green arrowheads, autofluorescence. Scale bars, 150 μm. (b) Oxidative DNA damage in cell nuclei at the dermal–epidermal junction is present in pigmented C57BL/6-HGF but not in albino FVB-HGF skin after ultraviolet A (150 kJ m−2). Scale bars, 10 μm. (c) Histogram of nuclear 8-oxodGuo (Volocity software analysis) of high-power confocal images of epidermal–dermal junctional skin. Nuclei counted (n) in C57BL/6-HGF: no ultraviolet 236, ultraviolet A 397; FVB-HGF: no ultraviolet 253, ultraviolet A 476. Comparison between four groups, P<0.001 (Kruskal–Wallis); all pairwise comparisons P<0.05 (Dunn's method). Significant nuclear 8-oxodGuo pixel intensity >20 arbitrary units (asterisk) is apparent only in ultraviolet A-irradiated C57BL/6-HGF skin. (d,e) Ultraviolet B (14 kJ m−2) was ineffective compared with ultraviolet A, at producing nuclear 8-oxodGuo in C57BL/6-HGF skin P<0.001 , Mann-Whitney. (Histogram, n=550). Scale bar, 10 μm. (f,g) Albino C57BL/6-c mice are not susceptible to nuclear 8-oxodGuo induction by ultraviolet A (150 kJ m−2), significantly different from nuclear 8-oxodGuo in ultraviolet A-irradiated C57BL/6-HGF skin, P<0.001, Mann–Whitney. (Histogram, n=300). Scale bar, 10 μm. Green is autofluorescence. (h) Neonatal pigmented melanocytes produce 8-oxodGuo in response to ultraviolet A (150 kJ m−2) but not to ultraviolet B (14 kJ m−2). Nuclear 8-oxodGuo was quantified as in panel c, but only in pigmented extra-follicular melanocytes, identified by the presence of black cytoplasmic melanin. 8-OxodGuo was significantly increased in C57BL/6-HGF melanocytes (n=92) after ultraviolet A, compared with no ultraviolet (n=32) or to ultraviolet B (n=57), P<0.001, Kruskal–Wallis. (i) Ultraviolet A irradiated (1.35 kJ m−2) cultured pigmented Melan-a melanocytes produce more 8-oxodGuo than albino Melan-c melanocytes. Scale bar, 250 μm. Histograms: 8-oxodGuo in Melan-a (n=524) compared with Melan-c (n=576), P<0.001, Mann–Whitney. 8-OxodGuo in unirradiated Melan-c or Melan-a cells (n>350 per cell line) was <6 units. Ultraviolet A dose was not phototoxic.