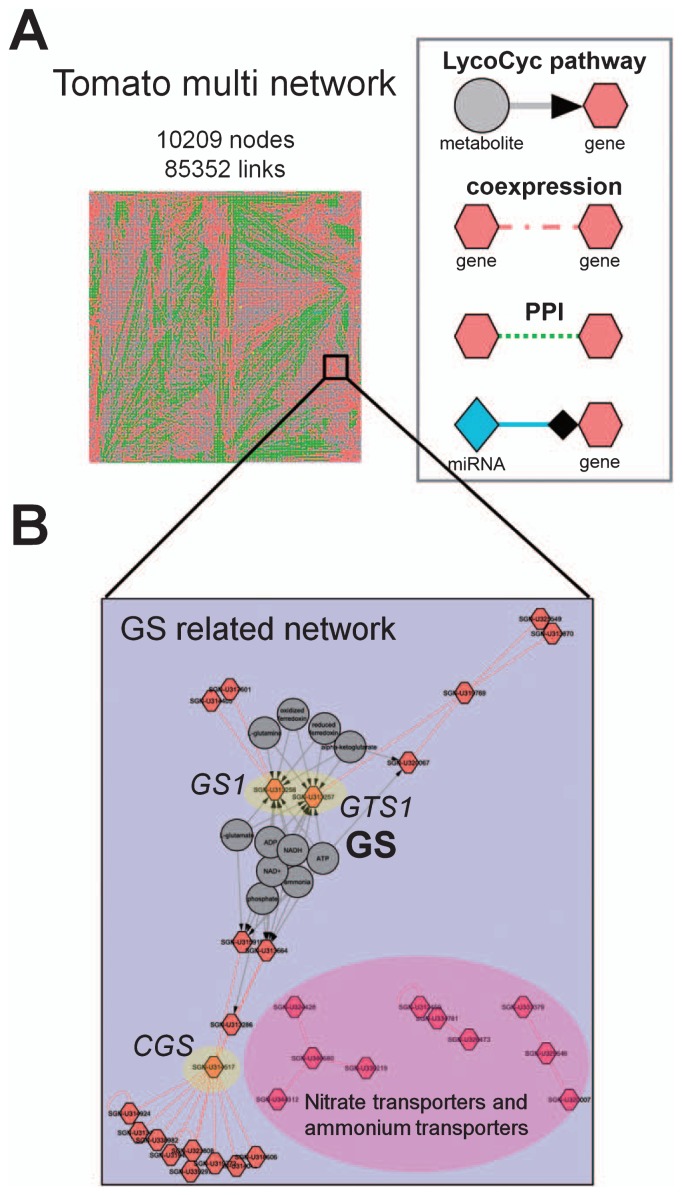
Fig. 3.
An example of a tomato multinetwork. (A) We constructed a tomato multinetwork that consisted of 10209 nodes and 85352 links. Information for the tomato metabolic pathway was obtained from the LycoCyc database (http://solgenomics.net/tools/solcyc/) (Mazourek et al. 2009), coexpression information (Fukushima et al. 2012), protein-protein interactions from interolog (Yu et al. 2004) and miRNA-gene relationships from PMRD (Zhang et al. 2010). (B) An expansion of the glutamine synthetase (GS)-related network in the multinetwork. Because the genes annotated as GS1 (SGN-U313258), GTS1 (SGN-U313257) and CGS (SGN-U314517) have many links to other genes, these genes are thought to be ‘hub’ gene candidates. PPI, protein-protein interaction; miRNA, micro RNA; GTS, putative GS; CGS, chloroplastic GS.