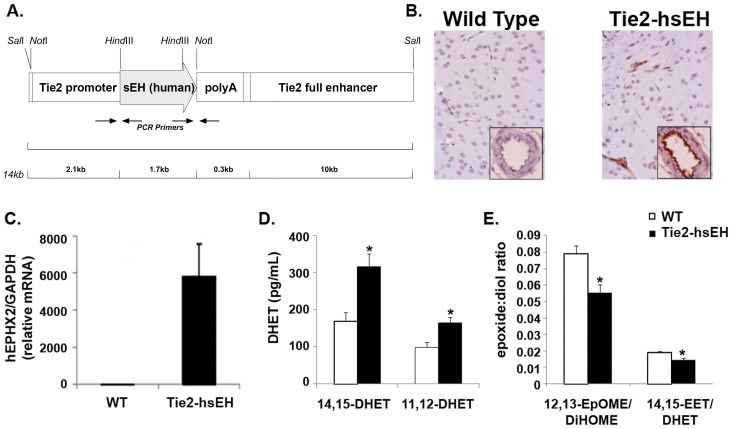
Figure 1. Characterization of Tie2-hsEH mice.
A. Schematic of the Tie2-hsEH transgenic construct used to generate mice used in this study. B. Sections of WT (left) and Tie2-hsEH (right) mouse brains immunolabeled for human sEH showing sEH in capillaries and large vessels in Tie2-hsEH. Inserts, blood vessels in cross section, show intense labeling in vascular endothelium in Tie-hsEH. C. Real-time PCR analysis of human sEH levels in brain tissue, showing presence of transgene expression in Tie2-hsEH and none in WT mice. D. LC-MS/MS analysis showing significantly increased 14,15- and 11,12- DHET plasma levels in Tie2-hsEH mice compared to WT (n = 8 WT, n = 13 Tie2-hsEH, P<0.05). E. LC-MS analysis of culture medium from WT and Tie2-hsEH aortic endothelial cells showing decreased ratios of 12,13-EpOME:DiHOME and 14,15-EET:DHET released by Tie2-hsEH endothelial cells compared to WT (n = 3 both groups, P<0.05).