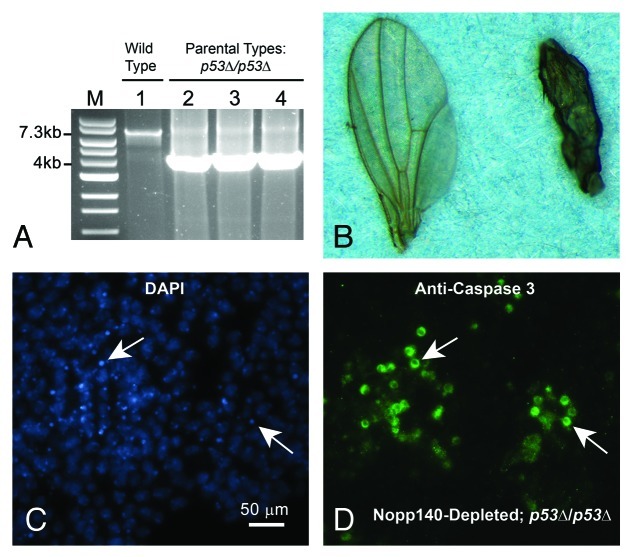
Figure 4. Verifying the p53 gene deletion in parental stocks and establishing p53-independent apoptosis in Nopp140-depleted wing discs. (A) The p53 gene deletion was verified using genomic PCR. The 7.3 kb band denotes presence of the wild type p53 gene while the 4.0 kb band denotes its deletion. Tested genotypes were: w1118 stock (wild type) (lane 1), A9-GAL4/A9-GAL4; +/+; p53∆/p53∆ (the GAL4 driver) (lane 2), the original p53∆/p53∆ stock (Bloomington 6815) (lane 3), w1118/w1118; UAS-C4.2/UAS-C4.2; p53∆/p53∆ (RNAi) (lane 4). (B) The cross reported in Table 1 was repeated using the A9-GAL4 and UAS-C4.2 lines that were homozygous for p53∆. Adult male progeny (w1118/Y; UAS-C4.2/+; p53∆/p53∆) again produced normal wings (left wing), while female progeny (A9-GAL4/w1118; UAS-C4.2/+; p53∆/p53∆) expressed RNAi to deplete Nopp140 and again displayed malformed wings (right wing). (C and D) Apoptosis was evident in the larval wing discs of A9 > UAS-C4.2; p53∆/p53∆ larvae as shown by anti-Caspase 3 labeling within the cytoplasm. White arrows point to corresponding nuclei containing condensed chromatin.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.