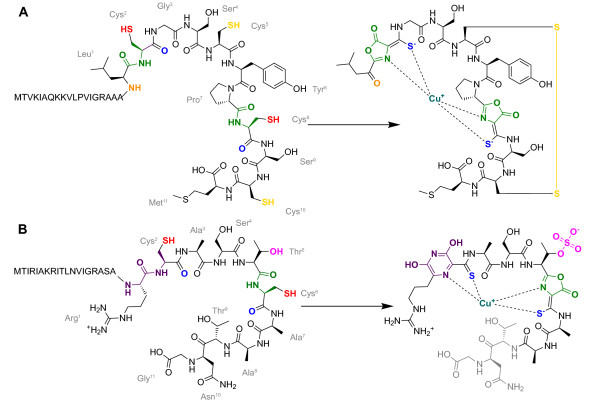
Figure 1.
Post-translational modifications required to produce methanobactins from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b and Methylocystis rosea SV97T. (A) Mbn from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b is generated from the precursor peptide MTVKIAQKKVLPVIGRAAALCGSCYPCSCM. Post-translational modifications needed to produce the final natural product include leader peptide cleavage and subsequent N-terminal transamination (orange), oxazolone formation (green), thioamide formation (blue), and disulfide bond formation (yellow). (B) Mbn from Methylocystis rosea SV97T is generated from the precursor peptide MTIRIAKRITLNVIGRASARCASTCAATNG. Post-translational modifications needed to produce the final natural product include leader peptide cleavage, pyrazinedione formation (purple) oxazolone formation (green), thioamide formation (blue), and threonine sulfonation (pink). Several residues that are present in the precursor peptide are missing in the reported structure (gray); the loss of a C-terminal threonine and asparagine had been previously reported, but identification of the precursor peptide indicates that a final glycine is also lost.