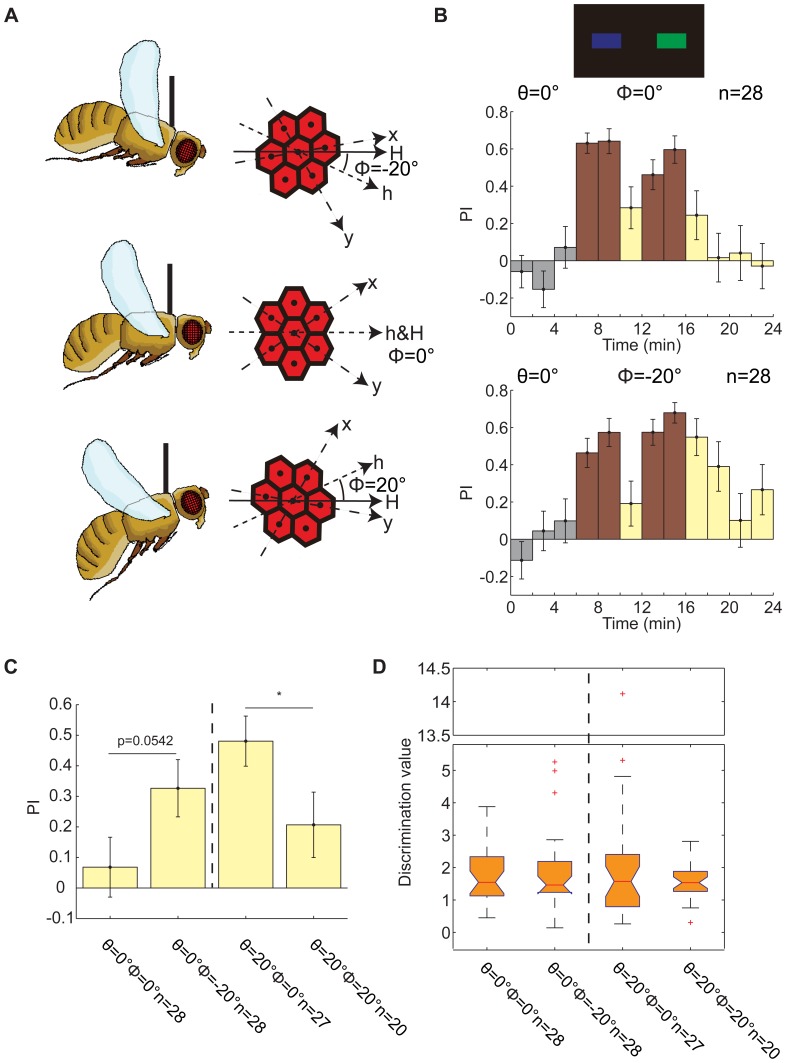
Figure 4. Learning effects can be altered by the elevation angles of tethered flies' heads.
(A) Schematic of tethered flies and their compound eyes with 3 elevation angles. h, the latitudinal axis of the ommateum; Φ, the elevation angle between h and the horizontal plane H. (B) Standard color memorization experiment in which patterns were presented on the vertical location Θ = 0°. Top panel, patterns used in this experiment. Middle panel, PIs of flies when the elevation angle Φ was 0°. The flies could not memorize which color was dangerous in this condition. Bottom panel, PIs of flies when Φ = −20°. Flies could memorize which color was dangerous in this condition. (C) The test PIs could be affected by the elevation angle at both locations (Θ = 0°; Θ = 20°). (D) The elevation angle had little influence on the flies' ability to discriminate colors. p = 0.9152 for the location θ = 0°; p = 0.8976 for the location θ = 20°. The y-axis of this chart is truncated for compactness. The data in (B&C) are given as the mean±SEM; the data in (D) are shown by box plot; the red crosses represent outliers; significant differences were calculated by the rank-sum test; * (p<0.05).