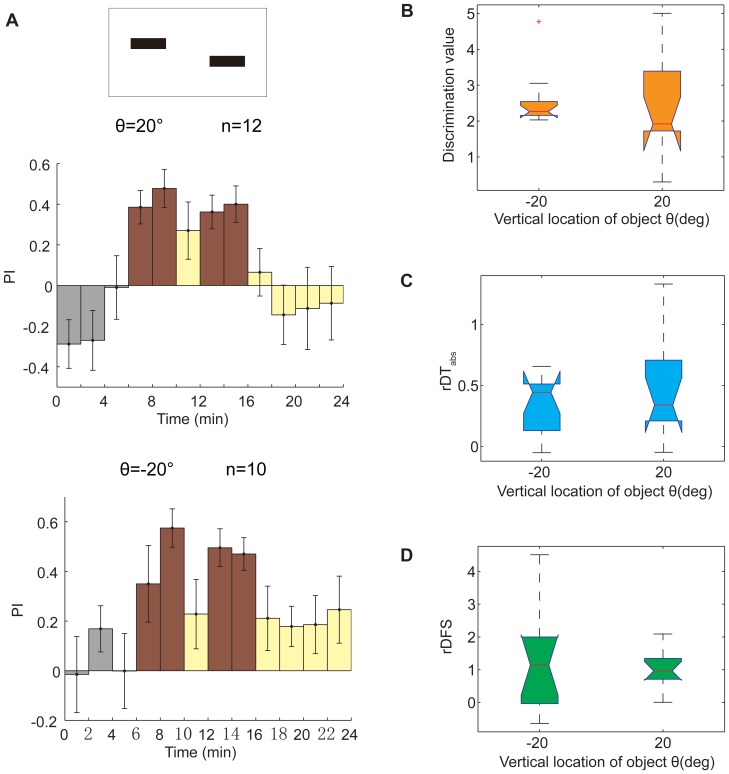
Figure 5. A lower location was preferred for COGs memorization against a white background.
(A) A standard 24 min visual operant conditioning experiment to memorize COGs with a white background. Top panel, patterns used in this experiment (ΔCOGs = 20°). Middle panel, PIs of flies when the patterns were 20° above them. The test PIs of the flies were not different from zero (p = 0.5186) in this condition. Bottom panel, PIs of flies when the patterns were 20° below them. Flies showed a tendency to avoid dangerous patterns in the test session for this condition. The test PIs at the location θ = −20° were higher than those at the location θ = +20°, although the difference was not significant (p = 0.0927). These PIs were not significantly different from zero (p = 0.084). (B–D) There was no significant difference in the other 3 indices between the 2 locations. (B) Discrimination value, p = 0.1563. (C) The rDTabs between safe quadrants and dangerous quadrants, p = 0.7667. (D) The rDFS between safe quadrants and dangerous quadrants, p = 0.8691. The data in (A) are given as the mean±SEM; the data in (B–D) are shown by box plot; the red cross represents outlier; significant differences between PIs and zero were judged by the signed-rank test; significant differences between 2 groups were judged by the rank-sum test.