Figure 1. A dual-perspective view on modeling individuals vaccination decision making.
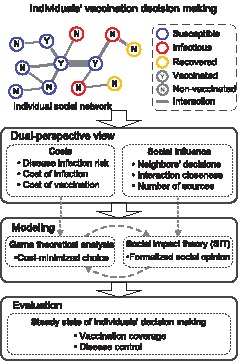
We extend the existing game-theoretical approaches by incorporating the impact of social influence. A group of interactive individuals can make decisions by both minimizing the associated costs and evaluating the decisions of others. We utilize social impact theory (SIT) to characterize the impact of social influence on individuals decision making with reference to their interaction relationships. We use a social contact network structure to represent individuals interaction relationships. By doing so, we can investigate the steady state of individuals decision making and examine the impact of social influence on vaccination dynamics and hence disease control, in terms of the vaccination coverage and the size of disease infections, respectively.
