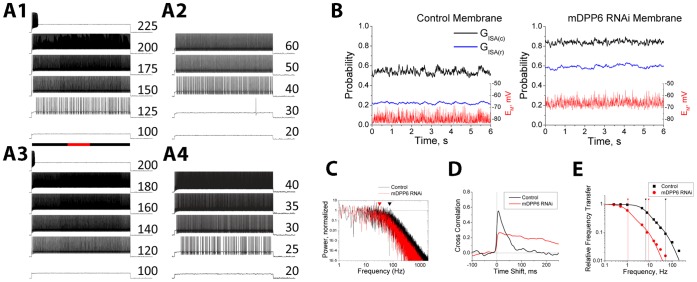
Figure 6. Co-regulation of Kv4 and TASK-3 channels by DPP6 optimizes the sensitivity of ISA to membrane potential fluctuations.
A) Firing properties of NEURON CG cell models. A1- Control, A2- CG(ΔTASK-3), A3- CG(ISA(R)), a4- mDPP6 RNAi. Current injection magnitude indicated to the right of the trace (pA). Black bar- injection duration, red inset- 1 s. A low level of random noise was added to these simulations (Ge = Gi = 10 pS; SDe = SDi = 50 pS). B) Effect of stochastic synaptic conductance fluctuations on ISA inactivation (Ge = Gi = 25 pS; SDe = SDi = 200 pS). In Control CG model, membrane potential fluctuates around −81 mV. Control ISA (GISA(c)) responds with fluctuations in inactivation near the 0.5 level. For mDPP6 RNAi ISA (GISA(r)) inactivation would be much less (∼0.2). In the mDPP6 RNAi CG cell, the mDPP6 RNAi ISA channel inactivation (GISA(r)) is near the 0.5 level, whereas a control ISA channel (GISA(c)) would be around (0.8). GISA(c) inactivation show higher frequency components than GISA(r). C) Power spectra for membrane potential fluctuations in Control and mDPP6 RNAi membranes calculated by FFT using OriginPro. Calculated corner frequencies for Control and mDPP6 RNAi membranes are indicated by triangles. mDPP6 RNAi signals fall off before Control due to a difference in membrane time constant. D) Cross-correlation analysis for ISA inactivation compared to membrane potential fluctuations. Control ISA shows a peak correlation of around 0.55 at 6.4 ms delay to the Control membrane potential fluctuations. For mDPP6 RNAi ISA, the peak correlation is 0.27 at a 15 ms delay to the mDPP6 RNAi cell membrane potential fluctuations. E) Frequency response properties for ISA channel inactivation. 5 mV sinusoidal waves from 0.25–200 Hz centered at −80 mV were fed into the GISA(c) and GISA(r) QuB channel models and the inactivation signal was measured and fit with a sine wave. The RMS amplitude of the fitted sine wave was compared to the inactivation produced by the RMS equivalent DC potential change of ±3.54 mV. The signal fall off at higher frequencies was fit with a double Lorentzian (corner frequencies indicated by drop lines). There is about a 7× shift to higher frequency responses when DPP6 is present in the ISA channel.