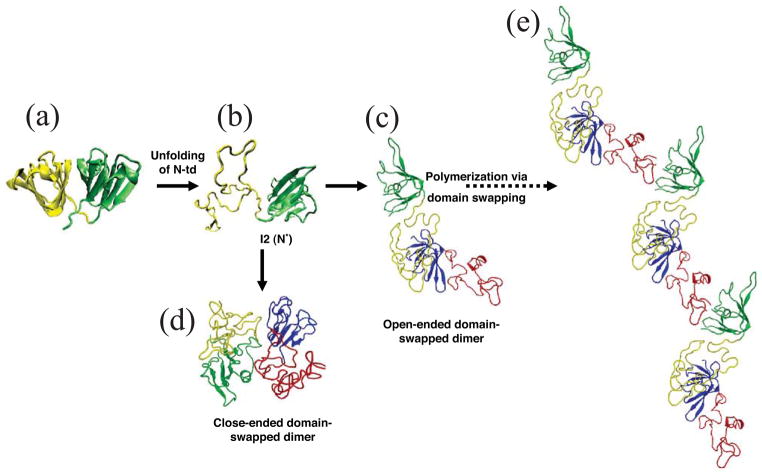
Figure 3.
Computational simulation of human γD-crystallin polymerization. (a) Crystal structure of human γD-crystallin. (b) Simulated monomeric aggregation precursor (I2), often referred as N* in the general mechanism of protein aggregation in literature. (c) Simulated structure of open-ended domain-swapped dimer. (d) Simulated structure of close-ended domain-swapped dimer. (e) Model of human γD-crystallin hexamer formed via domain swapping. Figure and legend reproduced with permission from [57].