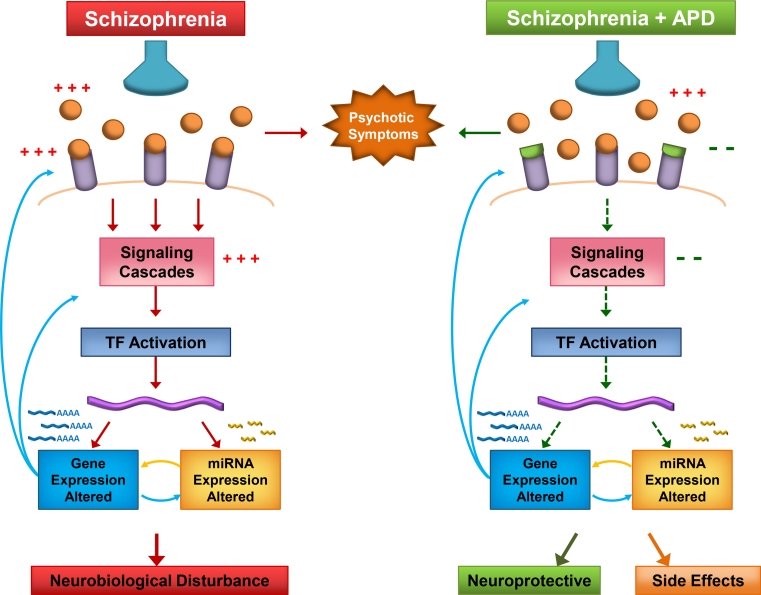
Fig. 3.
The potential involvement of miRNA in the underlying mechanisms of APD therapeutic action or side effects. Neurotransmitters (orange balls) are released by presynaptic receptors (blue funnels) and bind to their postsynaptic receptors (purple tubes) to induce signalling cascades. Transcription factor activation of DNA (purple waves) leads to altered miRNA and gene expression, including miRNA biogenesis genes. Mature miRNA modulate gene expression leading to further upstream changes and ultimately to changes in neurobiological processes. In schizophrenia, neurotransmitter receptor binding and signalling cascades are enhanced (three plus signs), resulting in the presence of psychotic symptoms. Recent findings support enhancement of miRNA biogenesis, with miRNA dysregulation leading to changes in gene expression, which results in neurobiological disturbances. APDs (green cups) block postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptors, relieving psychotic symptoms. Signalling cascades are tuned down (two minus signs), and opposing changes in miRNA and gene expression occur. The end result is modulation of pathways and processes that are neuroprotective, as well as those that, when altered, may be involved in the manifestation of side effects