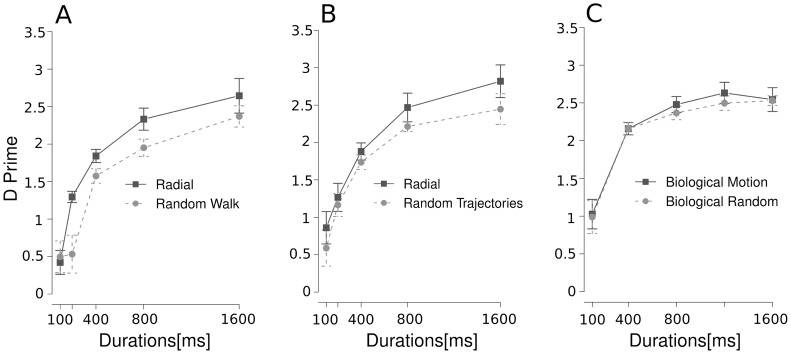
Figure 2. Detection of motion patterns under interocular suppression.
For each condition, d' is plotted as a function of dot duration. Patterns of dots moving coherently in radial direction towards the center had a higher detectability than patterns of random walk dots (experiment 1, panel A) or patterns of dots with random trajectories (experiment 2, panel B). A main effect of the type of motion was observed for both conditions. In contrast, meaningful biological motion did not lead to improved detection of suppressed motion over random biological motion (experiment 3, panel C).