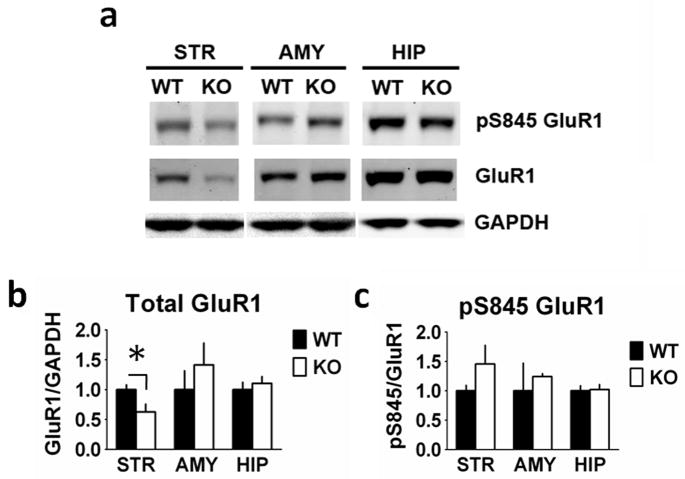
Fig. 5.
Glutamate receptor type 1 (GluR1) expression is reduced in the striatum from RCS knockout (KO) mice. Proteins from striatal (STR), amygdala (AMY) and hippocampal (HIP) extracts were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using GluR1, phospho-Ser845 GluR1 and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) antibodies. Representative immunoblots are shown in (A), and quantitation is shown in (B) and (C). Expression levels of GluR1 and phospho-Ser845 GluR1 were normalized to that of GAPDH. Error bars indicate SEM, n = 5–7 per group. Total GluR1 (F1,10 = 5.803, P = 0.037) levels were decreased in striatal homogenates from RCS KO mice compared with wild-type (WT) mice. There were no differences in amygdala (F1,11 = 0.291, P = 0.60) or hippocampal (F1,10 = 0.421, P = 0.53) GluR1 levels between WT and RCS KO mice. There were no differences in striatal pSer845 GluR1 levels when normalized to total GluR1 (F1,10 = 1.869, P = 0.20). In amygdala (F1,11 = 0.284, P = 0.20) and hippocampal (F1,10 = 0.33, P = 0.86) homogenates pS845 GluR1 levels were also unchanged.