Figure 1. Contact guidance of HUVEC cells on nanotopography.
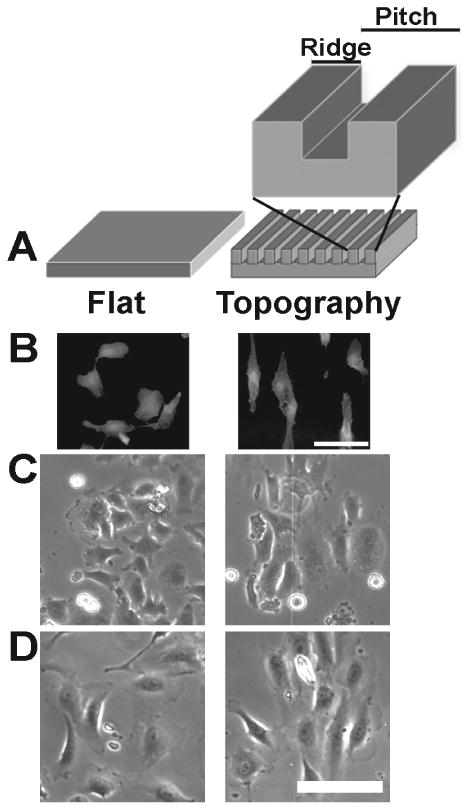
(A) A schematic representation of the control flat and anisotropic ridge and groove nanotopographic surfaces. The pitch is defined as the width from the start of one ridge to the start of the next ridge. (B) Fluorescence images of HUVECs that were fixed and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin 12 hours after plating on flat control and 400 nm topography surfaces. Individual cells on flat control exhibit no preferred orientation or alignment to the underlying substrate while HUVECs on 400 nm pitch exhibit contact guided orientation to the topographic cues. Phase contrast images demonstrating attachment and density of HUVECs plated onto flat control and 400 nm topographic surfaces (C) 1 hour and (D) 12 hours after plating. Scale bars = 100 μm.
