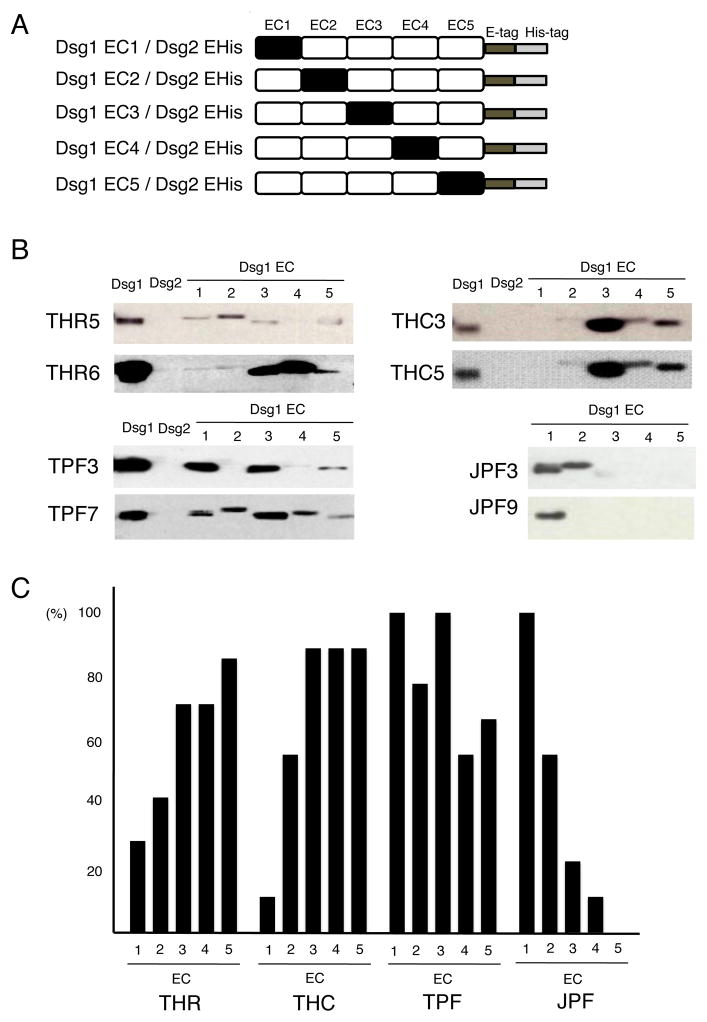
Fig. 3.
Epitope mapping using domain-swapped molecules.
(A) Schematic representation of domain-swapped molecules comprising EC domains of Dsg1 and the backbone of Dsg2. Domains EC1 to EC5 of human Dsg1 were domain-swapped with the corresponding domains of human Dsg2 to generate five recombinant molecules. (B) Representative results of epitope mapping of THR, THC, TPF, and JPF sera. Each serum sample was immunoprecipitated with rDsg1, rDsg2, and five recombinant domain-swapped molecules (labeled at the top of each panel) and subjected to immunoblotting using anti-E tag Abs. (C) Immunoreactivity of sera from each group (seven, nine, nine and nine from the THR, THC, TPF, and JPF groups, respectively) to each extracellular domain of Dsg1 (EC1 to EC5).