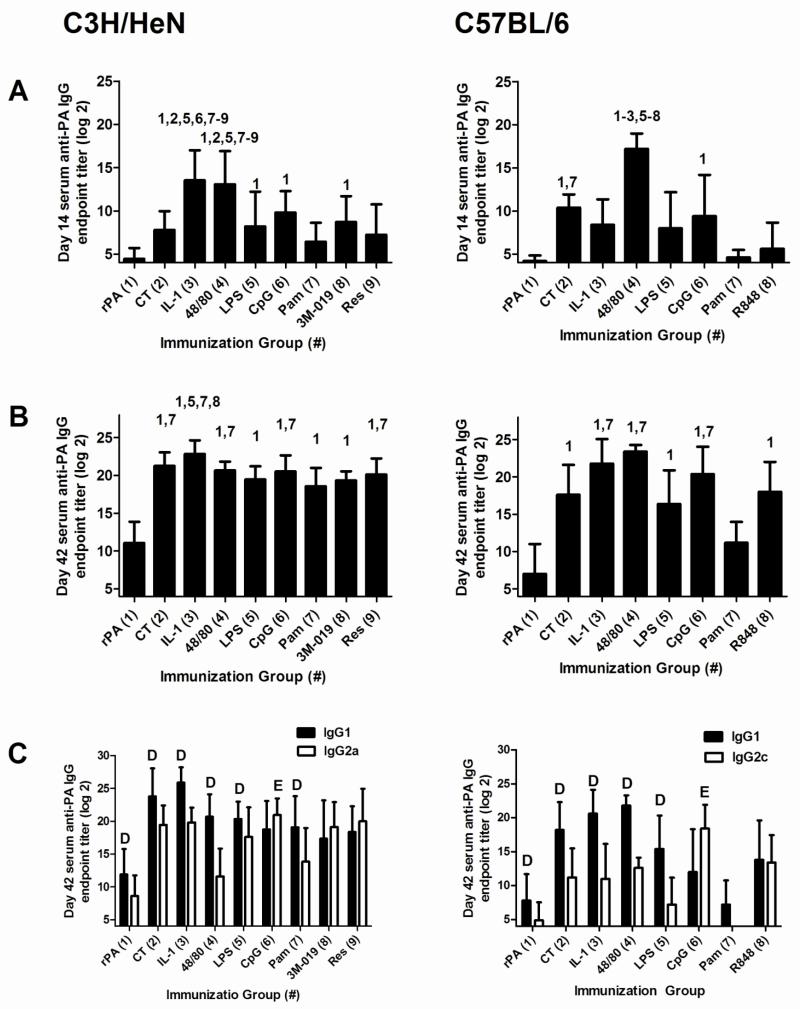
Figure 1. Nasal immunization with rPA formulated with non-toxin adjuvants induces antigen-specific serum IgG comparable to CT.
C3H/HeN or C57BL/6 mice were nasally immunized with rPA (2.5 μg) alone or rPA plus CT (1 μg), IL-1α (5 μg), c48/80 (15 μg), LPS (1 μg), CpG (10 μg), Pam3CSK4 (25 μg), 3M-019 (10 μg; C3H/HeN mice only) or resiquimod/R848 (10 μg) on days 0, 7 and 21. Serum was collected on days 14 (A) and 42 (B) and assayed by ELISA to determine anti-rPA IgG log2 endpoint titers. The data represents 2-3 combined experiments for C3H/HeN mice (n = 15 per group, except for the 3M-019 and resiquimod groups in which n = 10) and one experiment for C57BL/6 mice (10 mice in the antigen alone group, 5 mice in each adjuvant group). Bars represent mean ± standard deviation. For day 14 and 42 IgG titers, statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test. The numbers above the error bars indicate which groups (1-9) are significantly different from the indicated group. Day 42 samples were also tested for anti-rPA IgG1 and IgG2a/c responses (C). For day 42 IgG1 and IgG2a/c titers, paired Student’s T-test was used to compare IgG1 and IgG2a/c titers within each adjuvant group. D=IgG1 titer significantly greater than IgG2a/c titer within the same adjuvant group. E=IgG2a/c titer significantly greater than IgG1 titer within the same adjuvant group. Samples that had no detectable anti-rPA antibody were assigned a log2 value of one less than the starting log2 dilution for statistical analysis.