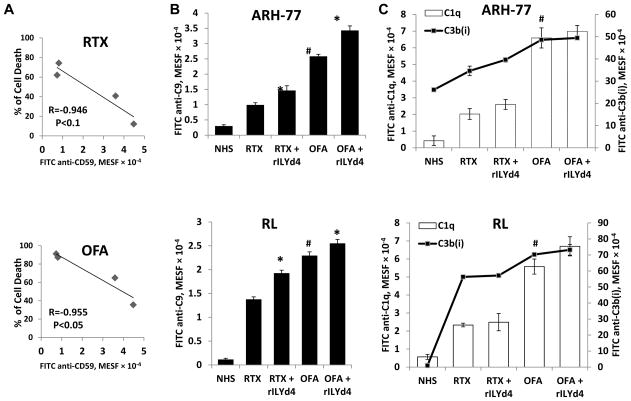
Figure 3. The CDC effect mediated by OFA correlates negatively with CD59 level and rILYd4 enhances C9 deposition on the cell surface of B-cell malignancy cells.
(A) Negative correlation between OFA-mediated CDC and CD59. (B) rILYd4 increases C9 deposition. ARH-77 and RL cells were treated with 10 μg/ml RTX or OFA in the presence of 20% NHS with or without 1074nM rILYd4. (C) C1q binding and C3b(i) deposition were not influenced by rILYd4. ARH-77 and RL cells were treated with 10 μg/ml RTX or OFA in the presence of 20% NHS with or without 1074 nM rILYd4. The levels of C1q binding and C3b(i) and C9 deposition were represented by MESF. (B–C) Result are mean ± SD of three different experiments. *: P<0.01 v.s. no rLYd4 treatment, #: P<0.01 v.s. RTX.