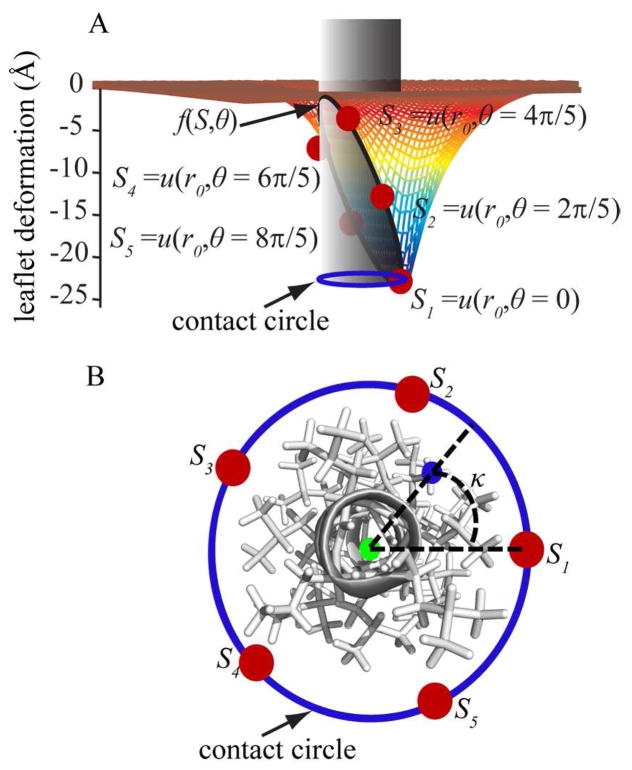
Figure 1.
(A) A schematic representation of an arbitrary deformation around a cylindrical solute inclusion in the top leaflet of the membrane bilayer. Fixed points at chosen angles (θ) around the contact curve where the membrane meets the solute cylinder (shown in gray) are indicated as red points. A cubic spline interpolation (f(S, θ)) of the leaflet deformation vs. θ is defined to calculate the deformation at any arbitrary point around the contact curve. The projection of the contact curve on an arbitrary plane parallel to the xy plane is shown with a blue circle. (B) Top view of the helix modeled with a cylinder in panel A. For an arbitrary atom marked with a blue point on the helix, the center of the contact circle is calculated as described in Eqs. 8 and 9 and shown with a green point. Then κ is calculated as explained in Eq. 10.