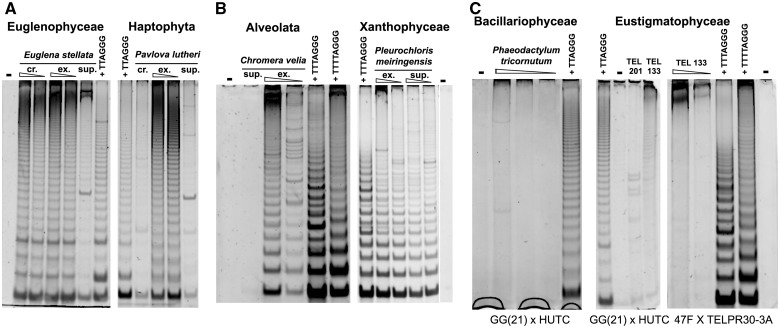
Fig. 3.—
Telomerase activity in algae outside Archaeplastida investigated by TRAP assay. Results of telomerase activity assay from representative samples of algal strains with telomerase synthesizing the human-type (A, Euglenophyceae, Haptophyta) and the Arabidopsis-type (B, Xanthophyceae, Alveolata) telomeric sequence, and those with negative telomerase activity (C, Bacillariophyceae, Eustigmatophyceae), are shown. The ladder of positive TRAP products (A, B) corresponds to 6- or 7-nt periodicity of control samples (human- and Arabidopsis-type, respectively). The efficiency of telomerase purification during preparation in protein extract (summarized in supplementary table S3, Supplementary Material online) was monitored (A, B) without PEG precipitation (crude, cr.), and in fractions nonprecipitated (supernatant, sup) and precipitated by PEG (telomerase extract, ex), protein extracts containing 100 ng and/or 1 μg of total protein were used. Negative results (C) were obtained using different amounts of total protein (indicated by triangle) from Phaeodactylum tricornutum (TEL231; 1, 0.5, 0.1 μg), Vischeria punctata (TEL201, 0.5 μg), and Eustigmatos polyphem (TEL133, 1, 0.1 μg on left and 0.5 μg on middle panel) and different primer combinations (indicated under panels). Combinations of the substrate primer GG(21) and the human-type repeat reverse primer HUTC (A, C) or of the substrate primer 47F and the Arabidopsis-type repeat reverse primer TELPR30-3A (B, C) were used. Telomerase-enriched extracts (50 ng of total protein) from Chlamydomonas hydra (TTTTAGGG), Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings (TTTAGGG), and Euglena stellata (TTAGGG) were used as a pattern control of an 8-, a 7-, and a 6-nt periodicity ladder, respectively; negative control (−), no extract.