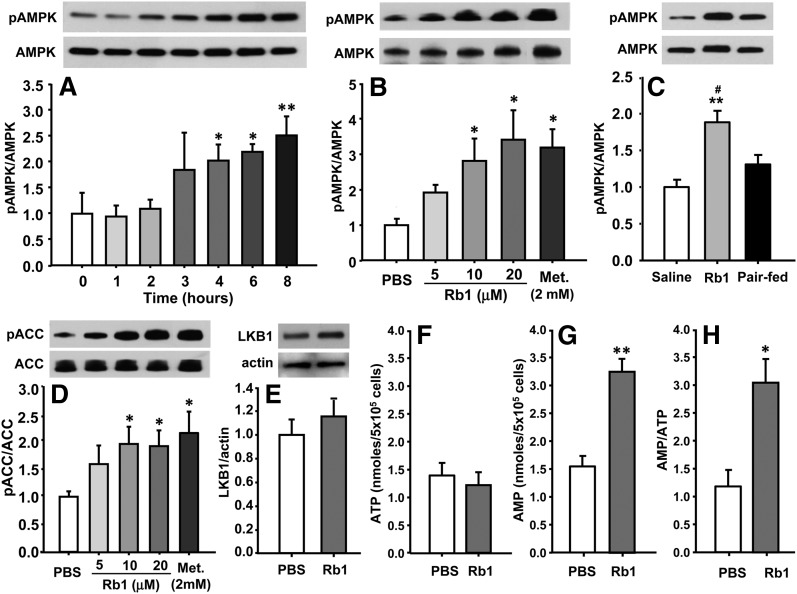
Fig. 4.
Rb1 time-dependently and dose-dependently increased the phosphorylation of AMPK (A, B) in cultured primary hepatic cells. In the time course study, overnight-cultured hepatic cells were treated with Rb1 (10 μM) for 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, or 8 h respectively. In the dose-effect study, the cells were treated with Rb1 at 5, 10, and 20 μM, metformin at 2 mM, or PBS for an additional 6 h. The increased phosphorylation of AMPK was confirmed in Rb1- or saline-treated HFD-induced obese rats (C). Rb1 also dose-dependently increased the phosphorylation of ACC (D). These measurements were conducted by Western blot. Top panels are representative immunoblots and bottom panels are quantitative analyses (A–E). To investigate the mechanisms mediating Rb1’s effects on the activation of AMPK, cultured hepatocytes were treated with Rb1 (10 μM) or PBS for 6 h. LKB1 protein levels were determined by Western blot and cellular AMP and ATP levels were measured by HLPC. Data are means ± SE (n = 3∼4 in in vitro study, n = 6 in in vivo study). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus vehicle control; and #P < 0.05 versus pair-fed animals.