Figure 2.
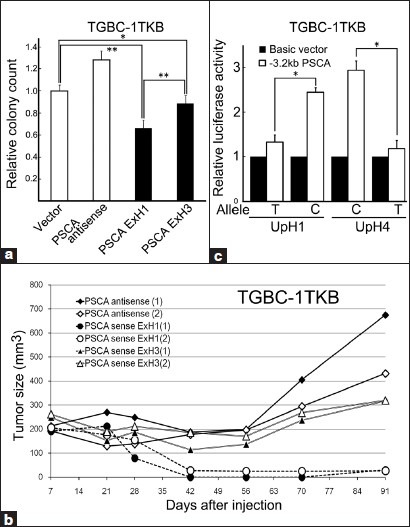
Single nucleotide polymorphism rs2294008 (T/C) influences both a cDNA function and a promoter activity of PSCA. (a) The cell-proliferation inhibition activity of PSCA ExH1 cDNA harboring the T allele was stronger than that of PSCA ExH3 cDNA harboring the C allele in vitro. The colony formation assay demonstrated that transfection of the PSCA ExH1 and ExH3 cDNAs to TGBC-1TKB reduced the colony counts ratio of the cell line to 0.66 and 0.89, respectively, of the reference, the cells transfected with empty vector. Error bars, standard deviation. *P < 0.01. **P < 0.001 (b) The tumor-formation inhibition activity of PSCA ExH1 cDNA was stronger than that of PSCA ExH3 cDNA in mice. TGBC-1TKB cells with stable PSCA ExH1 expression showed slower tumor growth in scid mice than did the cells with PSCA antisense or PSCA ExH3 expression. The diagram shows the transition of the size of the tumors (mean of the three injection sites). (c) The transcriptional activity of PSCA promoter was affected by the alleles of rs2294008. The luciferase reporter assay on two 3.2-kb upstream fragments of PSCA adjusted to Japanese haplotypes PSCA-UpH1 and UpH4 revealed that PSCA-UpH4 originally harboring the C allele had higher transcriptional activity than PSCA-UpH1 originally harboring T allele. Substitution of the C allele to T in the PSCA-UpH4 reduced the activity (UpH4 T) and substitution of T to C in the PSCA-UpH1 increased the reporter activity (UpH1 C). Error bars, standard deviation. *P < 0.05
