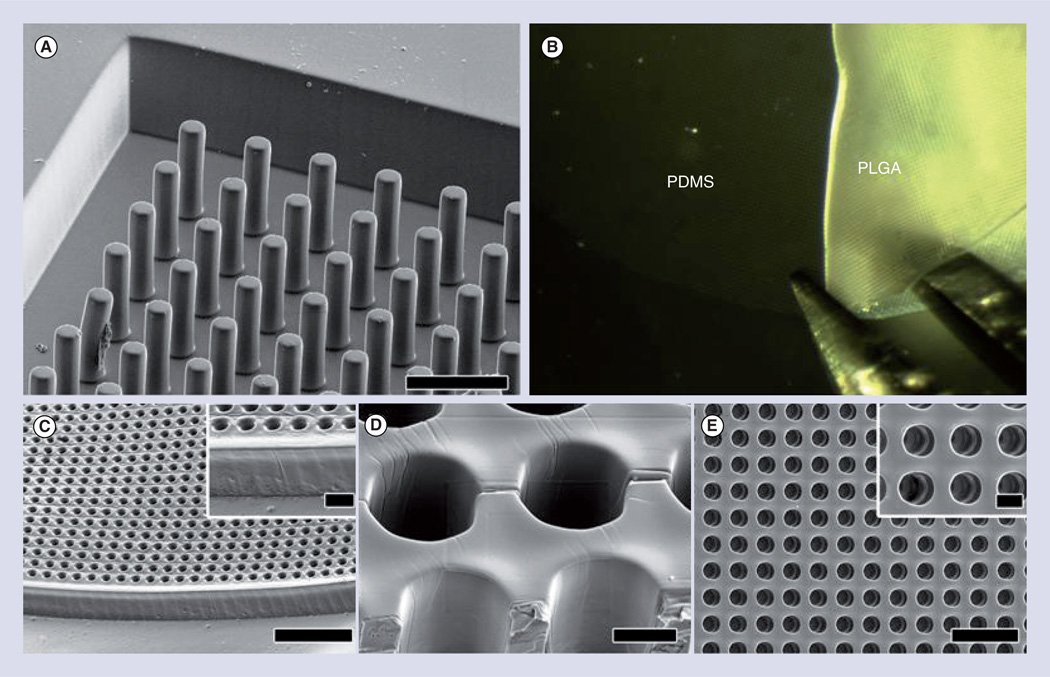
Figure 1. Microcylinder scaffolds are used to mimic the vertical structural organization of cells found in the retina.
(A) Scanning electron micrograph of PDMS negative mold. (B) Removal of PLGA scaffold from PDMS mold with forceps. (C–E) Scanning electron micrographs of top side of removed PLGA microcylinder scaffolds. (C) Overhead view. (C insert) Higher magnification of (C). (D) Alternate view at 45° tilt angle with cutaway showing inside walls of channels. (E) Alternate view at 45° tilt angle showing the edge of a scaffold. (E insert) Higher magnification of (E). Scale bars in (A) and (C) = 50 µm, (C insert) and (D) = 10 µm, (E) = 100 µm and (E insert) = 20 µm.
PDMS: Polydimethylsiloxane; PLGA: Polylactic-co-glycolic acid.
Reproduced with permission from [25]. © Elsevier (2012).