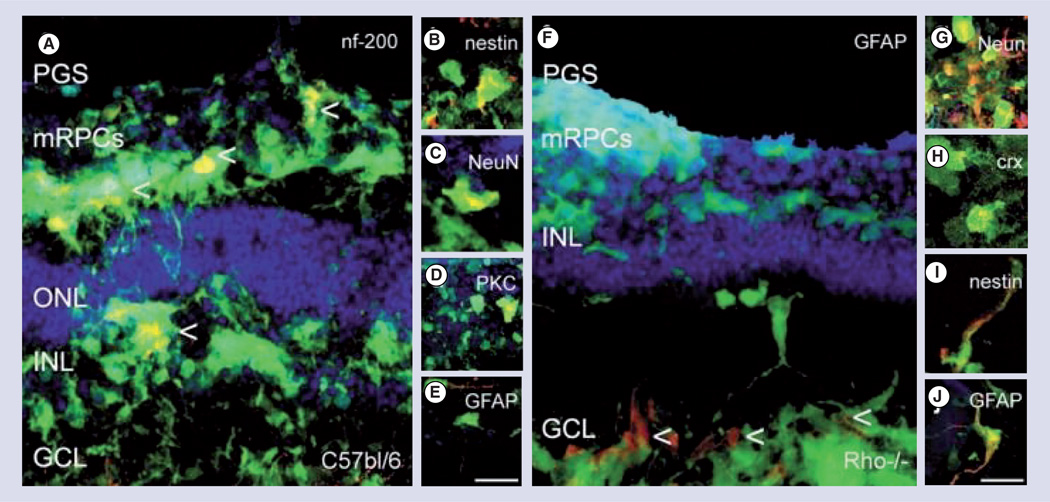
Figure 2. Polyglycerol sebacate microcylinder scaffold delivery of green fluorescent protein and retinal progenitors cells to control and rhodopsin knockout (Rho−/−) degenerated mouse retinal explants.
Retinal progenitors cells were capable of migrating to all layers of the retina and differentiating into several mature cell types (A–E) control wild-type retina, (F–J) Rho−/− retinas. (A) green fluorescent protein and mRPCs co-labeled (yellow) for nf200 (ganglion cell) labeled with arrows, (B) Nestin (immature), (C, G) NeuN, (D) PKC (bipolar), and (E,J) GFAP (glial) and (H) Crx (photoreceptor). Green: green fluorescent protein; red: rhodamine labeled marker; blue: topro-3 nuclei label; scale: 25 mm.
GCL: Ganglion cell layer; INL: Inner nuclear layer; NeuN: Neuronal nuclei; mRPCs: Murine retinal progenitors cells; ONL: Outer nuclear layer; PGS: Polyglycerol sebacate.
Reprinted with permission from [27]. © 2009 Elsevier.
Color figure can be found online at www.expert-reviews.com/doi/suppl/10.1586/eop.12.56