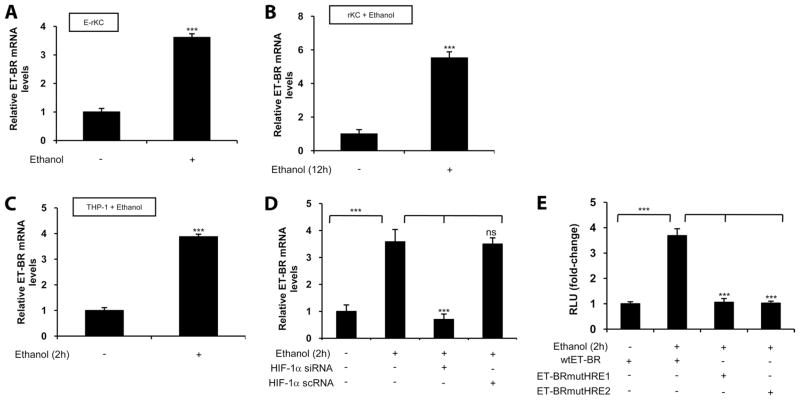
FIGURE 5.
Ethanol induces ET-BR expression in rKC and THP-1 monocytic cells via HIF-1α. A, Ethanol-induced ET-BR expression in Kupffer cells derived from ethanol-fed rats. The data represent fold increases in mRNA expression following ethanol feeding compared with control. B, Ethanol-induced ET-BR expression in ethanol-treated rKC. C, Ethanol-induced ET-BR expression in ethanol-treated THP-1 cells. D, Transient transfection of THP-1 cells with HIF-1α siRNA attenuates ethanol-induced ET-BR expression in ethanol-treated THP-1 cells. HIF-1α scrambled RNA was used as a control. Quantitative RT-PCR data for ethanol-treated rKC and THP-1 represent fold increases in mRNA expression following stimulation with ethanol (100 mM for 2 h) compared with no ethanol. All mRNA expressions were normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels, and the data shown represent three independent experiments (means ± SD). E, Ethanol-induced ET-BR promoter activity in THP-1 cells stimulated with ethanol, which was attenuated when two HRE sites were individually mutated. The data are expressed as fold change and have been normalized relative to the change in luciferase activity of the untreated controls and to the transfection efficiency with β-galactosidase. The data shown represent two independent experiments in duplicate (means ± D). ***, p < 0.001; ns, p > 0.05.