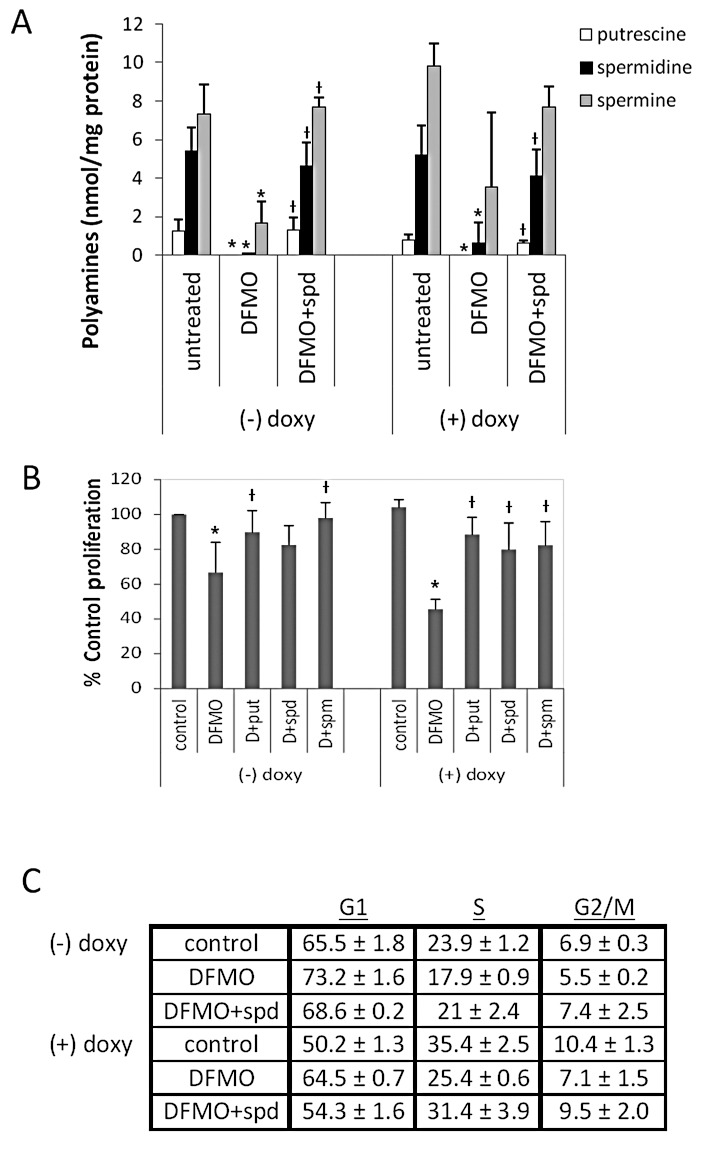
Figure 2.
DFMO inhibits polyamine biosynthesis, cell proliferation, and induces G1 cell cycle arrest in tetracycline-inducible MYCN overexpressing NB cells (MYCN2). (A) Cells were treated with doxycycline ± 5 mM DFMO ± 10 μM spermidine or left untreated for 72 h, and intracellular polyamine levels were measured. DFMO treatment depleted intracellular polyamine levels, and supplemental spermidine in culture media reversed the effects of DFMO. (B) Cells were treated with doxycycline ± 5 mM DFMO ± 10 μM putrescine, 10 μM spermidine or 10 μM spermine, or left untreated for 72 h, and cell proliferation was measured using the MTS assay. DFMO significantly inhibited proliferation in NB cells with and without MYCN overexpression. Supplementing external media with polyamines reversed the effects of DFMO. Results of (A) and (B) are represented as mean ± SD, n=3. *Statistically significant difference between values obtained from DFMO-treated vs. untreated cells. †Statistically significant difference between values obtained from DFMO-treated cells and cells treated with both DFMO and spermidine (P<0.05). (C) Cells were treated with doxycycline ± 5 mM DFMO ± 10 μM spermidine or left untreated for 72 h, and flow cytometry was performed with propidium iodide to quantify the percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle (G1, S, and G2/M). DFMO increased the percentage of cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, and supplementing external media with spermidine reversed the effects of DFMO. Results are represented as mean ± SD, n=3. Doxy, doxycyline; put, putrescine; spd, spermidine; spm, spermine.