Fig. 1.
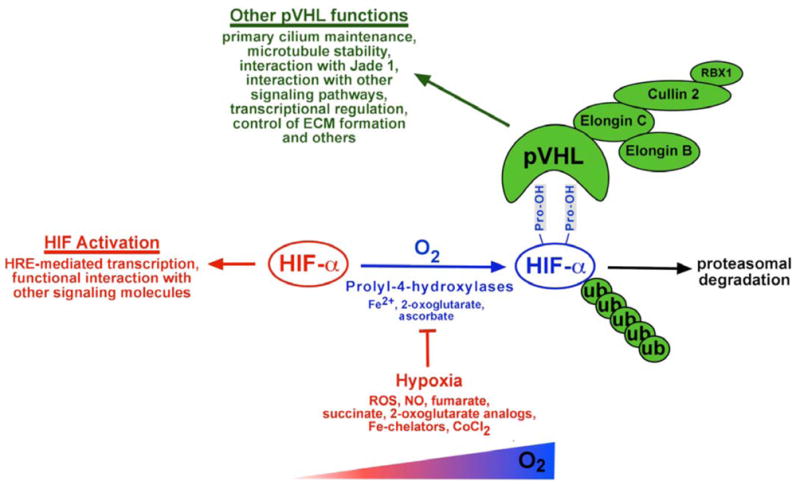
pVHL: master regulator of HIF. Schematic overview of pVHL functions. Aside from targeting HIF-α for proteasomal degradation, pVHL has multiple other functions. These include maintenance of the primary cilium, regulation of microtubule stability and interactions with several other signaling pathways. Binding to hydroxylated HIF-α occurs at the β-domain of pVHL, which spans amino acid residues 64 – 154. The C-terminal α-domain links pVHL via elongin C to the E3 ubiquitin ligase. Indicated are also conditions and molecules, which inhibit HIF prolyl-hydroxylation. Abb.: CoCl2, cobalt chloride; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ub, ubiquitin.
