Fig. 6.
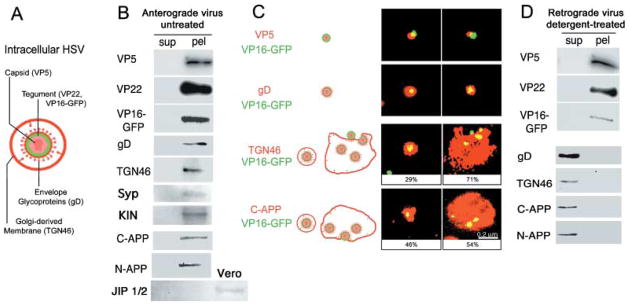
APP and TGN46 are associated with motile GFP-labelled HSV. (A) Diagram of HSV indicating the viral and host cell compartments recognized by the antibodies. (B) Cellular proteins co-sediment with GFP-HSV. Motile virus preparations were separated into particulate and soluble proteins by centrifugation and the resultant supernatants (sup) and pellets (pel) probed for proteins representative of each compartment by immunoblotting. Both viral and cellular proteins are detected only in the pellet: viral capsid (VP5), tegument (VP22), envelope (gD) and the VP16-GFP label (GFP), together with TGN46, a trans-Golgi marker, and APP detected with two different antibodies, one against the peptide in the cytoplasmic domain, C-APP, and the other against the extracellular domain, N-APP. Both anti-APP antibodies detected a single, ~120-kDa band in the pellet that could be superimposed in stripped and re-probed blots. Synaptophysin and kinesin are also detected in pellets of viral particles. JIP is not detected in either the supernatant or the pellet from the virus, but is present in the Vero cells (additional third lane from left). (C) Immunofluorescence shows that the cellular proteins, TGN46 and APP, are associated with GFP-labelled viral particles. Preparations of motile VP16-GFP-labelled HSV stained for viral compartments, capsid (VP5), envelope (gD), as well as cellular proteins (TGN46 and C-APP). Antibodies appear red, VP16-GFP-labelled HSV is green and overlap appears yellow. The GFP-label was associated with all three viral compartments, demonstrating that labelled particles represent intact virus. Appropriately, capsid (VP5) was within or beside the GFP, and envelope (gD) surrounded GFP label. GFP-labelled particles were also found associated with C-APP and TGN46. C-APP was apparently exposed on the particle surface, as it was detected without fixation or detergent. Both anti-TGN46 and anti-C-APP stain two different structures: small particles containing a single virus and large cisternae with multiple virions. Percentiles indicate the average proportion of each type of structure in motile viral preparations. The scale bar, bottom right, is the same for all images. (D) Detergent treatment which removes anterograde motility also separates APP from labelled viral particles. Motile preparations of GFP-labelled HSV were treated with Triton-X100 under conditions known to deplete anterograde and enhance retrograde motility (Bearer et al., 2000). Supernatants (sup) and pellets (pel) were separated by centrifugation and protein composition analysed by immunoblotting in parallel with untreated virus as shown in (B). Viral particles retained proteins representative of capsid and tegument (VP5, VP22) and the GFP label, whereas membrane components were solubilized (gD, TGN46 and APP). As in (B), APP was detected with two different antibodies, both of which detect a single band in the supernatant.
