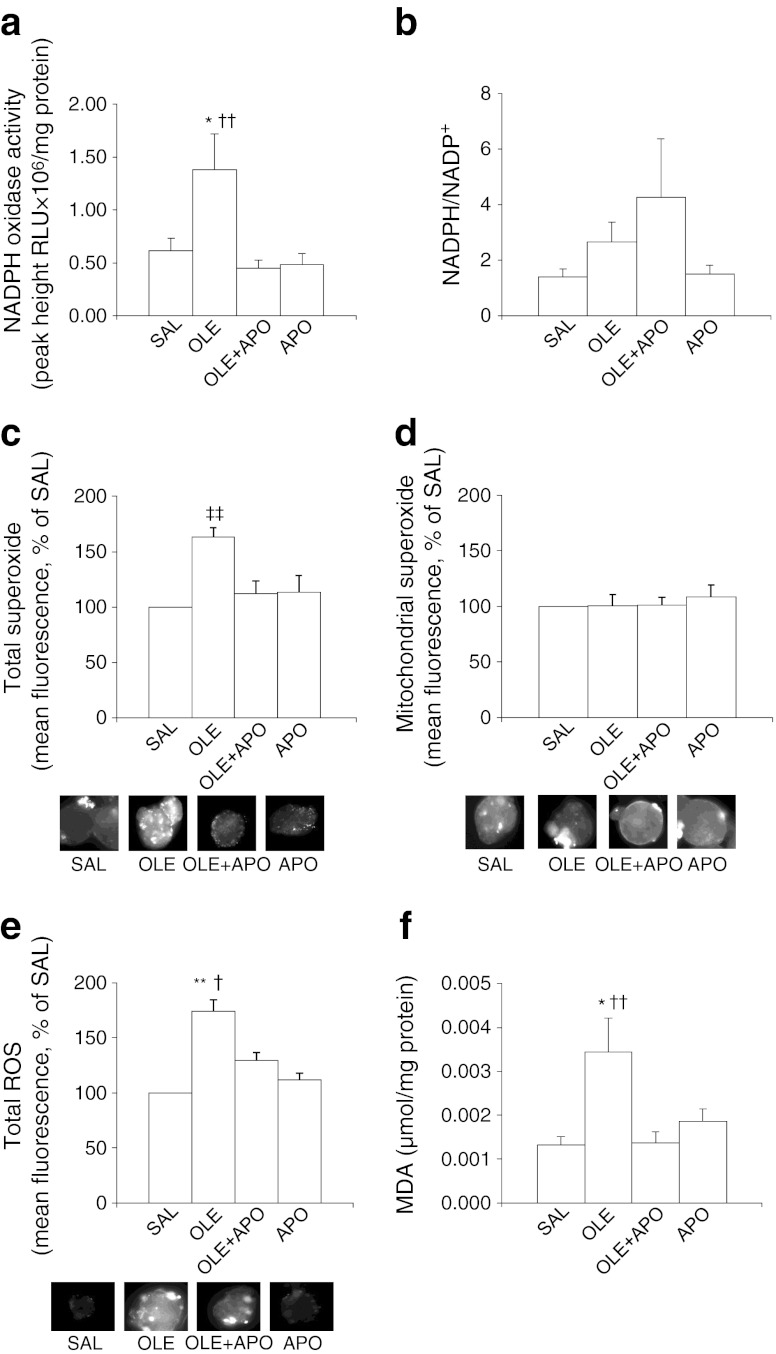
Fig. 1.
The NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin normalises NADPH oxidase activity, total superoxide, total ROS and MDA levels increased by oleate in rat islets. Rats were treated for 48 h with saline (SAL, 5 μl/min); oleate, to elevate plasma NEFA 1.5- to twofold (OLE, 1.3 μmol/min); oleate + apocynin (OLE + APO, 1.3 μmol/min + 0.5 μmol kg−1 min−1, respectively) or apocynin (APO, 0.5 μmol kg−1 min−1). (a) NADPH oxidase activity in freshly isolated islets of the rats treated as above. Data are means ± SEM (SAL, n = 7; OLE, n = 9; OLE + APO, n = 6; APO, n = 6). (b) NADPH/NADP+ in freshly isolated islets of the rats treated as above. Data are means ± SEM (n = 6 per group). Total (c) and mitochondrial (d) superoxide levels (n = 6 rats per group) and total ROS (e) levels (n = 4 rats per group) in freshly isolated islets of rats treated as above. Data are expressed as mean % of SAL ± SEM. The representative fluorescent images of islets stained with hydroethidine, MitoSOX and H2DCF-DA are also shown. (f) MDA levels in freshly isolated islets of rats treated as described above. Data are means ± SEM (SAL, n = 7; OLE, n = 8; OLE + APO, n = 9; APO, n = 9); *p < 0.05 OLE vs SAL, **p < 0.01 OLE vs SAL, † p < 0.05 OLE vs OLE + APO and APO, †† p < 0.01 OLE vs OLE + APO and APO, ‡‡ p < 0.01 OLE vs all